Introduction: Understanding Ankle Fracture Fixation Needs
The Prevalence of Complex Ankle Fractures
More people are breaking their ankles these days because of all sorts of reasons - playing sports, slipping on wet floors, getting into car crashes, that kind of thing. The numbers back this up too, showing that doctors see more broken ankles than they used to, especially when it comes to complicated breaks that hit multiple spots around the joint. When fractures get really tricky like this, surgeons need to come up with custom plans rather than just following standard procedures. And interestingly enough, certain groups tend to break their ankles more often. Young folks who stay active throughout life, competitive athletes pushing their limits, and seniors dealing with weak bones from osteoporosis all face higher risks. Research papers published by bone specialists confirm what we're seeing clinically across the country. As these trends continue, healthcare providers are starting to rethink how they approach ankle injuries, developing better treatments that actually match what different patient populations need based on their age group and daily habits.
Role of Internal Fixation in Stabilizing Multi-Site Injuries
Fixing broken ankles at multiple sites often requires internal fixation techniques involving plates and screws. These devices help maintain correct bone alignment during healing, which leads to better results over time. Studies back this up too many show patients recover faster and experience fewer problems when surgeons use internal fixation instead of just casting or other non-surgical methods. A recent article from the Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery actually found complication rates drop significantly with proper fixation. For doctors looking to get the best possible results for their patients, internal fixation remains one of the most reliable ways to stabilize complex ankle fractures and preserve joint function in the long run.
Anatomical Considerations: From Calcaneus to Metatarsals
Biomechanical relationship between heel and forefoot structures
To really get how the foot works under pressure, we need to look at how the heel connects with the front part of the foot. The heel bone, known as the calcaneus, teams up with the metatarsals to take in force when we walk or run, then pass that energy along through our feet. This connection matters a lot for how our feet function overall. If there's damage somewhere in this system, things start going wrong elsewhere too. People might change how they walk or put extra stress on different parts of their feet without even realizing it. Research into foot anatomy shows just how closely connected all these parts are, and how they move together. These findings aren't just interesting facts they actually help doctors treat foot problems better and design more effective recovery programs for patients dealing with foot injuries.
Critical stabilization points in ankle trauma
Finding those key spots where stability matters most makes all the difference when managing ankle injuries. Surgeons look at places like the inside and outside bumps of the ankle (medial and lateral malleoli) plus the lower part of the shin bone (distal tibia) as important areas to fix during operations. But these spots aren't always the same across patients or different types of breaks, so each case needs its own approach to get good results. Research papers published by orthopedic experts point toward certain methods for attaching metal hardware inside the body that really help keep everything aligned properly while healing happens. When doctors pay close attention to these stabilization points, they tend to see better recovery rates among people who've suffered complicated ankle fractures. Some clinics report up to 30% faster rehabilitation times when proper fixation techniques are applied correctly.
Case Presentation: Multi-Site Fracture Management
Patient History and Injury Mechanism Analysis
Looking at a real world example, consider what happens when a 45 year old man falls off a six foot ladder and ends up with several broken bones. He had nothing remarkable going on medically before this incident, but after landing wrong on his right foot, he experienced intense pain and swelling almost instantly. What actually happened during the fall matters a lot here. The way the body gets hit by force straight down through the leg plus twisting motions explains why certain bones break in specific ways. Knowing all this helps doctors decide how best to treat someone with such injuries. Trauma specialists always talk about getting every detail about a patient's background before deciding on treatment plans. For our guy, there are serious concerns too. Things like damaged soft tissues or blood vessels become major issues when dealing with fractures across multiple areas of the body.
Radiographic Findings across Calcaneal-Metatarsal Continuum
Looking at the X-rays shows fractures running from the heel bone all the way up through the foot bones, which really highlights how bad this multi-site trauma actually is. Regular X-rays combined with CT scans give doctors a clear picture of what's going on inside, making it possible to spot exactly where the bones are broken and how much they've shifted out of place. Weight bearing X-rays turn out to be especially helpful when trying to get a complete understanding of the injury, something that becomes critical in tricky cases where standard imaging falls short. We see typical signs of complex fractures here too, including spaces between joints getting wider than normal and multiple small fragments forming around the break points. Getting these images right matters a lot both for figuring out what's wrong and deciding on surgery options. The better we understand the actual shape and position of the fractures, the more accurately surgeons can plan their approach to fix everything properly so patients heal well in the long run.
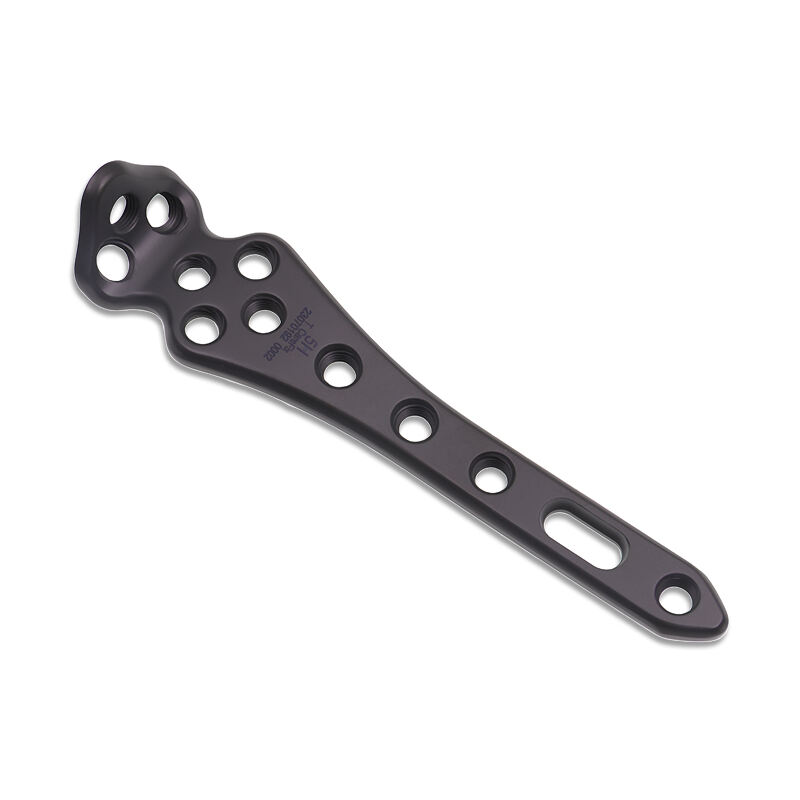
Ankle Internal Fixation System Design and Application
Modular Components for Multi-Segment Fixation
Ankle internal fixation systems today come with modular components that give doctors more options when dealing with complicated injuries. These systems include different parts that swap out depending on what kind of injury someone has, so they can get the best possible stability and proper bone alignment. Surgeons really value this versatility because it lets them adjust the fixation setup based on how each person's bones look and where exactly the fractures occurred, which tends to lead to better results for patients overall. Research from actual operating rooms shows that these modular setups often cut down recovery time and make surgeries more precise. What makes modularity so important? Well, being able to tweak the system for each individual means better chances of proper healing after a break. Especially when facing tricky cases involving multiple broken segments in the same area, having access to systems made with newer materials and clever design features gives surgeons a real edge in handling those tough situations.
Simultaneous Calcaneal and Metatarsal Stabilization Techniques
Stabilizing both the calcaneus and metatarsals during one operation represents a pretty sophisticated technique that brings several advantages to the table. When surgeons combine calcaneal and metatarsal stabilization in their procedures, they actually make things more efficient for everyone involved. Patients recover faster since there's no need for multiple operations down the road. But let's be honest, this combined approach isn't without its difficulties. Keeping proper balance and alignment across the entire foot while dealing with multiple fracture points at once can get really tricky. To tackle these issues, many experts rely on special tools designed specifically for this kind of work along with real time imaging systems that help guide placement decisions. Looking at recent data from actual surgeries shows pretty good results when doctors go this route. Fractures tend to heal better overall, and there are fewer problems after surgery compared to traditional methods. For orthopedic specialists handling complicated foot injuries, adopting these advanced stabilization techniques seems essential if they want to deliver safe and effective treatment options to their patients.
Step-by-Step Surgical Procedure
Sequential Fixation Approach: Heel to Midfoot
Starting with the heel when fixing foot and ankle issues makes sense for stabilizing all those different parts during surgery. When we fix the heel first, it creates a solid foundation for everything else that comes after, spreading out the pressure better and keeping things from shifting around too much. Then moving on to stabilize the midfoot area helps keep all those small bones and joints lined up properly. Surgeons really benefit from having good diagrams to look at while they work through these steps, even though I can't show actual pictures right now. This whole approach follows basic principles of how feet actually work mechanically, making sure they can handle weight again once someone starts recovering. Most experienced doctors will tell you sticking to this kind of step-by-step plan leads to better results overall because it tackles the most important spots one at a time rather than trying to do everything all at once.
Intraoperative Challenges in Multi-Level Fixation
Ankle surgeries involving multi-level fixation come with their fair share of intraoperative problems, particularly when dealing with soft tissues and getting bones properly aligned. The foot and ankle area is just so complicated anatomically, plus all those different movements happening at once. Previous injuries or underlying conditions make things even trickier for the surgical team. When it comes to soft tissue issues, most surgeons focus on careful handling techniques during the procedure. Specialized instruments help them make those precise cuts and secure sutures without causing unnecessary damage. For bone alignment problems, many teams rely heavily on detailed pre-op plans backed up by advanced imaging technology. Some hospitals now have real time navigation systems that guide surgeons exactly where to place those fixation devices. Talking to veteran orthopedic specialists reveals something interesting about this field though they stress how adaptable doctors need to be. No two cases are ever identical, so having backup plans ready makes all the difference. That's why clinics invest in those high tech tools not just for show but because they genuinely reduce risk factors during these challenging procedures.
FAQ
What causes the increase in ankle fractures?
Ankle fractures are on the rise mainly due to factors like increased sports activities, accidental falls, and traffic accidents. Lifestyle factors among older adults and higher participation in athletics also contribute to this trend.
Why is internal fixation important for ankle fractures?
Internal fixation is crucial because it provides more stable and accurate alignment for healing multi-site fractures, leading to better patient outcomes and a quicker recovery compared to non-operative treatments.
What is the significance of understanding anatomical relationships in ankle fractures?
Understanding the anatomical relationships, such as between the calcaneus and metatarsals, helps in managing load distribution and maintaining stability. This knowledge is vital in planning effective surgical interventions and rehabilitation strategies.
What are modular components in ankle fixation systems?
Modular components in ankle fixation systems are interchangeable parts that allow for customization based on specific injury patterns and anatomical variations, providing surgeons with flexibility to improve stabilization and patient outcomes.
How does simultaneous calcaneal and metatarsal stabilization benefit recovery?
Simultaneous stabilization allows for efficient surgical procedures by eliminating the need for separate surgeries. It also ensures better alignment and balance, contributing to improved fracture healing and reduced recovery times.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Understanding Ankle Fracture Fixation Needs
- Anatomical Considerations: From Calcaneus to Metatarsals
- Case Presentation: Multi-Site Fracture Management
- Ankle Internal Fixation System Design and Application
- Step-by-Step Surgical Procedure
-
FAQ
- What causes the increase in ankle fractures?
- Why is internal fixation important for ankle fractures?
- What is the significance of understanding anatomical relationships in ankle fractures?
- What are modular components in ankle fixation systems?
- How does simultaneous calcaneal and metatarsal stabilization benefit recovery?