Introduction: Adult Knee Deformities and the Need for Correction
Understanding Varus and Valgus Malalignment
The two main knee deformities seen in adults are varus and valgus malalignments. When someone has varus alignment, their knees tend to bow outwards creating what looks like an O-shape between them. Valgus works differently though it pushes the knees inward so they form an X pattern instead. Beyond just changing how legs look, these issues actually put extra strain on joints over time. Research shows people with these misalignments face much higher chances of developing osteoarthritis down the road, particularly when nothing gets done about it early on. Knowing what symptoms to watch for matters a lot because catching problems sooner rather than later makes all the difference. Getting familiar with warning signs helps protect long term joint function and stop things from getting worse before they even start causing pain.
Impact of Untreated Knee Deformities on Joint Health
Failing to fix knee deformities can really harm joint health over time. When the bones aren't properly aligned, people tend to experience more pain and instability in their knees, which eventually wears down the joints themselves. Studies show that leaving these problems unaddressed might actually reduce how long a person's knee will last before needing replacement. The risk goes up for things like torn meniscus and worn cartilage when alignment stays bad for months or years. Many patients end up needing procedures like High Tibial Osteotomy surgery to get things back in line and regain normal movement. That's why catching and treating these deformities early makes all the difference in avoiding serious damage and keeping knees healthy longer.
What Is High Tibial Osteotomy (HTO) Surgery?
Biomechanical Principles of HTO
High Tibial Osteotomy or HTO for short involves cutting and moving parts of the shin bone to realign the knee joint. Surgeons perform this operation mainly to take pressure off worn out cartilage while spreading weight more evenly across the knee. Why does this work? Well, basic body mechanics explain it all, especially when talking about how forces get distributed. When done right, proper alignment after HTO surgery really helps people suffering from knee arthritis. Most report less pain and better movement in their joints. Studies back this up too showing that simply moving where the stress hits inside the knee makes a big difference. Patients typically notice less discomfort day to day and tend to slow down how fast their joints deteriorate over time.
Indications for HTO in Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis
High tibial osteotomy works best for adults dealing with osteoarthritis in the inner part of their knee joint, particularly people younger than 65 years old whose knees bow outwards due to what doctors call varus deformity. Most medical professionals suggest considering HTO after other non-surgical approaches haven't worked anymore, which usually means someone still experiences ongoing discomfort and struggles with basic movements despite trying different therapies. For many patients, this procedure offers a real alternative if they wish to stay physically active but aren't ready for full knee replacement surgery just yet. Getting accurate information about how bad the misalignment actually is makes all the difference when deciding whether HTO fits the bill. That's why thorough assessments tailored specifically to each individual case remain so important throughout the decision making process.
Patient Selection Criteria: Age, Activity Level, and Alignment
When it comes to picking good candidates for HTO surgery, doctors look at several factors including age, how active someone is, and their knee alignment. Most people who benefit from this procedure tend to be around 40 up until about 65 years old. They're generally pretty active too, maybe running or doing sports regularly. What these patients want is to keep their knees working well for as long as possible before they have to consider something more drastic like total replacement. Checking just how active a person really is gives surgeons a better idea if the operation will work out well for them down the road. X-rays and other imaging tests are absolutely essential for figuring out exactly where the misalignment is happening in the knee joint. These images show precisely what's going on inside so the surgeon knows exactly which areas need correction. By focusing on these specifics during planning, medical teams create treatment strategies tailored specifically to each patient's unique situation, which often leads to much better results after surgery.
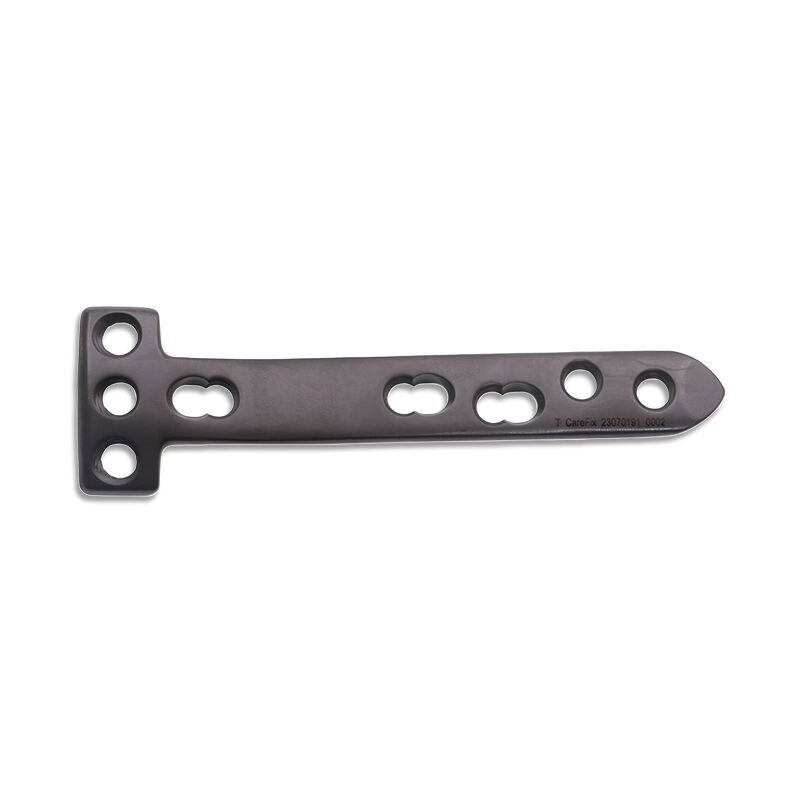
HTO Locking Plate Design: Engineering for Stability and Precision
Key Features of Modern HTO Locking Plates
HTO locking plates today come with design improvements that make them much better at stabilizing bones during surgery and improving overall results. They feature things like angular stability and various screw configurations that give surgeons more flexibility when placing implants. Most modern plates use titanium alloys or other biocompatible metals that last longer inside the body, cutting down on the chances of the implant breaking down over time. Clinical studies show these newer designs lead to better stability after surgery, which means patients tend to heal faster and experience fewer complications following High Tibial Osteotomy procedures. Surgeons who have switched to these advanced plates report noticeable differences in patient recovery times and long term joint function.
Biomechanical Advantages of Locking Compression Plates (LCP)
Locking compression plates, or LCPs as they're commonly called in orthopedic circles, offer some real biomechanical benefits that surgeons love. The way these plates work is pretty clever actually – when the screws lock into place inside the metal, it creates much better stability across the fracture site and spreads out the weight more evenly throughout the bone. Research looking at actual clinical outcomes shows that LCPs tend to hold up better during osteotomy procedures than regular non-locking plates do, which explains why so many operating rooms have switched to them. And there's another plus point worth mentioning: when used specifically for high tibial osteotomies (HTO), these plates cause far less irritation to surrounding soft tissues compared to traditional methods. That means patients generally heal faster without all the extra inflammation and discomfort that comes from improper hardware placement.
TomoFix Plate: A Gold Standard in Rigid Fixation
Among orthopedic surgeons performing HTO procedures, the TomoFix plate has become something of a benchmark thanks to how well it matches the natural shape of the tibia bone. Studies from various clinics point to pretty impressive success rates when this plate is used, particularly regarding proper bone healing after surgery. What really sets it apart though is the strong hold it provides once implanted. This rigidity means fewer problems down the road following surgery, which translates to better healing experiences for patients in the short term and generally good results years later. Many doctors report their patients recover faster and experience fewer setbacks compared to other fixation methods.
Surgical Application of the HTO Locking Plate
Preoperative Planning with 3D Patient-Specific Instrumentation (PSI)
Good preoperative planning really matters when it comes to using HTO locking plates effectively, and now 3D patient specific instruments are changing how surgeons approach these preparations. With 3D modeling tech at their disposal, doctors get to see exact replicas of what they'll be working on inside the body. This lets them map out every detail before making any incisions. The result? Surgeries tend to go much smoother, take less time overall, and the implants end up in just the right spots. Looking at clinical data from various medical centers shows something interesting too. When hospitals started incorporating these custom made guides based on individual scans, complication rates dropped significantly while recovery times improved across the board for people who had HTO surgeries.
Step-by-Step Technique: Osteotomy Execution and Plate Fixation
HTO surgery involves two key components: performing the osteotomy cut and securing it with plates. Surgeons need to make accurate cuts during the osteotomy procedure, then carefully position and fix the plates so everything lines up correctly at the right angles. Getting these details right matters because even small mistakes can lead to problems down the road or delay recovery times. After surgery, following established protocols is just as important. Regular check-ups help track how well the bone is healing around the osteotomy site while making sure the plates stay put where they're supposed to be. Most patients find that sticking to these guidelines makes all the difference in their overall recovery process.
Integrating Bone Grafts and Synthetic Materials for Enhanced Healing
Adding bone grafts together with man made materials really helps speed up recovery after HTO surgery. Both real bone taken from the patient and lab made alternatives work well to help the bones grow back together properly at the cut site. Looking at all the research out there, most studies show that when doctors combine grafts with HTO operations, patients generally have better mobility in their joints and face fewer problems after surgery. Knowing what different graft options exist allows surgeons to pick the right mix for each case, which makes a big difference in how well someone heals over time. Experience shows this approach leads to much better results down the road for people who need these kinds of corrections.
Clinical Results: Outcomes of HTO Locking Plate Utilization
Pain Reduction and Functional Improvement Post-Surgery
A lot of people who suffer from knee pain choose to have High Tibial Osteotomy or HTO for short, and most find that their pain goes down quite a bit while they also notice better movement and function in their knees. When looking at how well this works, patient feedback remains one of the best ways to measure progress. Research shows around 8 out of 10 patients feel much better within about twelve months after getting the procedure done. These numbers matter because they help surgeons understand if things are going right and where maybe some changes need to happen with follow up treatment. Keeping an eye on how patients recover allows doctors to adjust treatments as needed so everyone gets the best possible outcome from their surgery.
Radiographic Success: Achieving Optimal Joint Alignment
Getting the joints properly aligned after HTO surgery really matters for how well the whole procedure works out. X-rays and other imaging techniques help doctors figure out if everything lines up right along the mechanical axis of the leg. Studies show time and again that when joints are aligned correctly, patients tend to have better joint health years down the road. That's why these measurements aren't just numbers on a scan they actually predict future problems. Follow up scans are pretty much standard practice now. They let surgeons keep an eye on how stable the joint remains after surgery. The images give doctors something tangible to look at when assessing recovery progress. If things start going off track, early detection means timely intervention before bigger issues develop.
Long-Term Survival Rates and Delay of Knee Arthroplasty
High Tibial Osteotomy offers both short term relief and looks pretty good over time since it might actually put off the need for knee replacement surgery. Research indicates that when done right, HTO can really prolong how long knee joints last. About 80% of people who get this operation still have functioning knees after several years, which makes HTO a solid choice for younger folks looking for something besides full knee replacement. Tracking what happens to patients long after their surgery helps doctors learn more about whether this treatment works well in the real world. Delaying knee replacement surgery comes with definite advantages too. Patients typically enjoy better knee function for many extra years without having to go through big operations down the road.
FAQ Section
What are the main types of knee deformities in adults?
The main types of knee deformities in adults are varus malalignment, which causes the knee to bow outward, and valgus malalignment, where the knee tilts inward.
What complications can arise from untreated knee deformities?
Untreated knee deformities can lead to increased pain, instability, and joint degeneration. They may result in complications such as meniscal tears and cartilage wear, necessitating surgical interventions like HTO.
Who are ideal candidates for High Tibial Osteotomy (HTO) surgery?
Ideal candidates for HTO are typically between 40 to 65 years old with a moderate to high activity level, and they seek to prolong knee function and delay more invasive procedures.
What are the advantages of using HTO locking plates?
HTO locking plates offer enhanced fixation stability and better surgical outcomes, reducing the risk of implant failure and promoting healing through features like angular stability and multiple screw options.
How does 3D patient-specific instrumentation improve HTO surgeries?
3D patient-specific instrumentation allows for precise planning by accurately simulating the patient's anatomy, improving implant accuracy and reducing operation time, leading to better postoperative outcomes.
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Adult Knee Deformities and the Need for Correction
- What Is High Tibial Osteotomy (HTO) Surgery?
- HTO Locking Plate Design: Engineering for Stability and Precision
- Surgical Application of the HTO Locking Plate
- Clinical Results: Outcomes of HTO Locking Plate Utilization
-
FAQ Section
- What are the main types of knee deformities in adults?
- What complications can arise from untreated knee deformities?
- Who are ideal candidates for High Tibial Osteotomy (HTO) surgery?
- What are the advantages of using HTO locking plates?
- How does 3D patient-specific instrumentation improve HTO surgeries?