Introduction: Lumbar Spine Conditions Requiring Fusion
Disorders of the lumbar spine present significant challenges to health and function, frequently requiring surgical intervention including fusion of the spine. Most commonly, degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, and traumatic insult are common causes of spinal instability. Intervertebral discs gradually wear out, causing pain and instability – this is called degenerative disc disease. Spondylolisthesis, with its one vertebrae slipping forward, also contributes to spinal instability. Other causes can be trauma related (such as accidents or heavy impact) that weaken the structure and/or function of the spine. These comorbidities impact significantly a considerable proportion of the population, emphasizing the demand for feasible approaches to treat these comorbidities. Lumbar spine instability breaks up overall mobility and overall quality of life, sending so many people looking for solutions such as intervertebral fusion devices.
Common Pathologies Leading to Spinal Instability
A number of common lumbar conditions contribute to unstable spines, leading to reduced movement and reduced quality of life. These include degenerative disk disease, spondylolisthesis, and traumatic injury. Degenerative disc disease is essentially the wearing-out of the disc, causing pain and limiting the disc’s ability to work. With spondylolisthesis, a misalignment of the vertebrae moves the bones out of position on top of one another, resulting in instability. Missile-related injury results in trauma to the spinal column and may produce early instability. These conditions are highly prevalent, collectively affecting millions, and resulting in the need for surgery frequently, as per the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. With the progression of these pathologies, instability is induced in the lumbosacral spine, which prevents patients from leading an active life and may necessitate an intervertebral fusion implant to restore stability and mobility.
Goals of Lumbar Fusion Surgery
Objective Lumbar fusion is performed to improve spinal stability, to reduce pain, and to restore function. This type of surgery is particularly useful for people who have instability from a degenerative condition or a traumatic episode. Recent literature also report marked advances in patient outcomes following surgery, such as significant decrease in disability rates and improvements in daily functioning. The goals of lumbar fusion surgery are to help support the spine, reduce chronic pain and enhance the patient's quality of life. The latter targets dovetai well with our patients’ goals of returning to activities of daily living, or even sports. All because the lumbar fusion procedure stabilizes the spine so individuals can take back control of their bodies, feel better and have enough energy to get back to enjoying life.
What Is an Intervertebral Fusion Device?
Design and Material Innovations
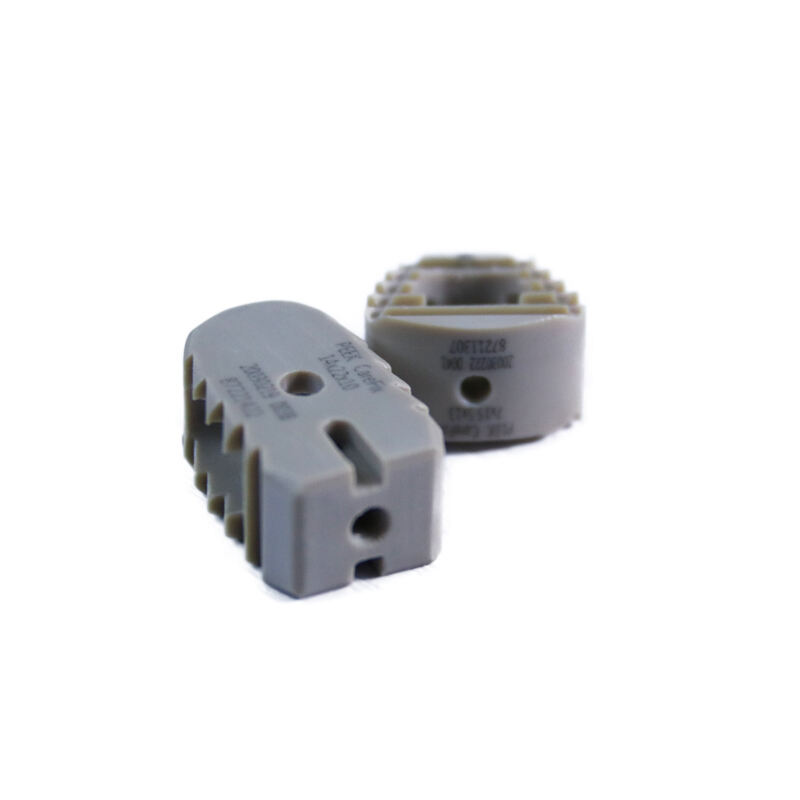
Intervertebral fusion implants are of great importance in spinal fusions, and are commonly employed to stabilize and enhance the fusion of spinal motion segments. Such devices usually have patterns that encourage new bone to grow as well as help stabilize the spine. Advancements in materials, including titanium and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), have significantly improved biocompatibility and fusion rates. These advancements have provided data from orthopaedic journals showing that the durability of the devices redeemed patient outcomes which correlated with successful spinal fusion surgeries. It will be appreciated that the use of bone-mimetic materials, such as those made of PEEK, can promote a successful spinal fusion by way of proper bone in-growth and a reduction in stress shielding. This progress allows patients recovering from lumbar issues to return to an active lifestyle quicker.
Biomechanical Role in Spinal Stabilization
[0002] Intervertebral fusion devices support the spinal column and provide biomechanical stabilization of the spine while facilitating bony fusion of the adjacent segments when positioned between vertebrae. They do so with proper distribution of the load to minimize the stress in the vertebral bodies and the risk of excessive movement at the site of fusion. Central to these devices, is the capacity to reduce stress shielding – a process which can result in the decrease in bone mass around the device. They maintain structural integrity of the spine by reducing axial loads through restoration of the normal anatomy. Studies have shown that these devices, commonly called intervertebral cages, greatly enhance mechanical stability after surgery, which has the patients back to their normal activities sooner and decreases the chance of re-injury. Such mechanical support is particularly important when treating lumbar spine pathologies which frequently result in instability of a patient's spine and such patient's ability to ambulate.
Types of Lumbar Fusion Surgical Approaches
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF)
ALIF (anterior lumbar interbody fusion) is well known to have specific advantages in lumbar fusion surgery. It appears that the major benefit of the ALIF procedure is a minimization of muscle damage in gaining access to the spine from an anterior approach, contributing to less recovery. This is typically less painful after surgery than other approaches. Clinical studies have shown that the success rate of ALIF is very high and ALIF plays an effective role in bone fusion. Researchers suggest that ALIF is typically the procedure of choice for patients with certain anatomical issues that can be best addressed by treating them from the front.
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF)
It is a procedure that relies on a posterior exposure to the spine and lumbar for access to the vertebral bodies as well as the disc space. It relies on a series of operative steps that are designed to accurately position grafts into the intervertebral space with advantages in terms of structural support and reduction in mobilization. Recent reports indicate that PLIF leads to high patient satisfaction and good results of spine diseases. It is especially applicable to spinal canal stenosis and with the aid of the Posterior approach offers improved decompression of compressed nerves in these situations.
Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF)
TLIF (Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion) is well known for the least invasive technique and maximized advantages that can be achieved in lumbar fusion procedures. This approach allows for spinal fusion with less tissue trauma and faster recovery times with superior pain management following surgery. TLIF vs ALIF and PLIF: TLIF has become the preferred option by most clinicias due to its patient recovery time and its postoperative pain management. Patients who are ideally suited for TLIF are usually best illustrated by the type of cases where they give you the best indication which includes those that require fine anatomical targeting of lumbar pathology without the need for wide surgical exposure. All in all, TLIF is most remarkable because it is a personalized lumbar spine solution.
Surgical Procedure Overview
Preoperative Planning and Imaging
Preoperative preparation and imaging are essential in lumbar fusion surgeries. Image modalities, such as MRI and CT enabled the arrival of new imaging for enhanced surgical planning. They aid surgeons in locating the exact location and nature of spinal deformity and aid in the success of the surgery. Studies have shown that appropriate preoperative imaging improves the accuracy of surgery and reduces the risk of complications. In addition, interdisciplinary cooperation between neurologists and radiologists is important. Their knowledge provides for a thorough evaluation, consistent with personalized surgical approaches that fit the needs of the particular patient. This team model has been an excellent resource in the continued effort of enhancing patient care and surgical outcomes.
Step-by-Step Implantation Process
A sequence of steps can be of importance in the lumbar fusion operation for both accuracy and efficiency. After the patient is anesthetised, the procedure is to follow. Incisions are then made by the surgeons to gain access to the target segment of the spine and then the intervertebral fusion devices are carefully implanted. The statistics make it clear that each step is critical: good surgeries will improve recovery and survival rates. Once again, a lumbar fusion procedure on average, takes between 3- 6 hours and recovery will be measured in weeks. Surgical precision is of the essence; it not only saves surgical time, but also prevents postoperative complications. This delicate process is essential in achieving good results and improving the patient's quality of life after surgery.
Intraoperative Navigation Technologies
Intraoperative navigations are considered as one of the important means to improve the accuracy of the lumbar fusion. Real-time visualization is possible thanks to tools such as fluoroscopy and computer-aided surgery systems that help surgeons to perform accurate interventions. Studies has also shown that these technologies can greatly enhance the surgical success with reduced complications. The use of such high-tech navigation tools is in line with the increasing preference for minimally invasive surgeries, which are associated with faster recovery times. The future of surgical technology And what lies ahead for surgical technology is even more exciting. Technologies like bad reality and robotics will continue to improve30lumbar fusion so that more precise, safer, and better results are possible.
Device Application in Lumbar Fusion
Cage Placement and Distraction Techniques
Sterile interbody devices used to restore the intervertebral space after discectomy for lumbar fusion are critical for achieving optimal results. At least in part due to the strategic placement of these cages and effective distraction techniques, it is advantageous to maintain or enlarge intervertebral space, necessary for fusion and alignment. It has been reported that the improvement in the cage placement could greatly improve the fusion success. Procedures such as posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) deploy the cages with the aim to gradually achieve fusion and stability by filling in the disc space. Proper caging restores normal spinal curvature and biomechanical function, which leads to fewer post-operative complications and an expedited recovery.
Distraction techniques are also very crucial in lumbar fusion, they assist surgeons to create a large space where implants are to be placed. The appropriate amount of distraction not only permits easier cage insertion and placement but also allows nerve root decompression, which in turn reduces postoperative pain and leads to improved recovery. For example, the deployment of dedicated instruments serves to distract the intervertebral space incrementally for minimal trauma to surrounding tissue. Thus, patients often have reduced postoperative pain and a more rapid return to normal activity.
Bone Graft Integration Strategies
Bone grafting techniques are essential to the success of lumbar fusion procedures because they support the body's own fusion between the vertebrae. Bone grafts, whether autografts, allografts or synthetic substitutes, each confer distinct respective advantages according to patient variability. Autografts are obtained from the patient’s body and are known for its high biocompatibility and successful integration. Concurrently, donor-derived allografts are preferable to address the need for shorter operating times and obviating the creation of a second surgical wound.
The decision to use one type of bone graft versus another is based on proven efficacy in enhancing fusion and reducing reoperation rates. The use of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) as synthetically produced substitutes for promoting bone growth and fusion has been reported, for example. Choosing the correct graft is then based on the status of the individual patient, patient's age and the lumbar disease involved, to guarantee the best or personalized fit of bone graft material. These strategic choices are critical to prolong the survival of the fusion and to maximize the patient results.
Clinical Outcomes and Long-Term Efficacy
Fusion Success Rates Across Approaches
The success of fusion rates of various types of operations (ALIF, PLIF and TLIF) is variable and method dependent, influenced primarily by surgical skill and experience. Newer studies seem to indicate small differences between the procedures, but ALIF may have the highest fusion rate. For example, ALIF generally reports a similar fusion rate of approximately 90% at the 1-year time point, which is supported by a number of studies confirming the efficacy of this approach. In comparison, PLIF and TLIF share comparable rates that range from 85-88% at the same 12 month interval. These differences emphasize the role of the surgeon's experience; experienced surgeons are able to mitigate the complications and improve the global outcome. This is important because, in addition to bone growth, the success of fusion is closely associated with reduced pain and increased mobility, and the type of approach is crucial to the way the patient recovers.
Postoperative Pain Reduction Metrics
Decreasing pain in the postoperative period is an important measure of the success of a lumbar fusion. Pain scale measurement scores and patient satisfaction questionnaires are usually the most common jouney's destination. For instance, large improvements of pain scores from 7 before the operation to 2 after the operation were reported for procedures such as TLIF, illustrating good efficacy. These results are frequently reflected in the satisfaction rate of the patient, who say that the quality of their life has improved after surgery. Nevertheless, age, comorbidities, and type of fusion technique can influence pain results. For example, patients who are younger or have less chronic disease typically experience a more rapid relief of pain. This demonstrates the importance of identifying and considering patient profiles when maneuvering to improve pain control through surgical treatment.
12-Month Recovery Timeline Analysis
The long-term effectiveness of the surgery is heavily influenced by several key events through the period of the average 12 month recovery time the average lumbar fusion patient will experience. In the beginning some pain reduction is noted within a few weeks after the completion of the surgery. Most will begin physical therapy by the third month, emphasizing increasing strength and mobility. At 6 months, a significant proportion of patients have returned to usual activities, albeit with some restrictions. “Evidence based guidelines demonstrate that a structured rehabilitation approach during this time has a massive impact on the speed and quality of recovery.” Recovery, however, is variable and depends on things like age, general health, and compliance with rehabilitation. Although most patients improve significantly by 1 year, the heterogeneity of patient recovery indicates that patient-specific recovery plans should be considered in order to achieve maximal rehabilitation and maintain benefits in the longer term.
FAQ
What are the main lumbar spine conditions requiring fusion?
Degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, and trauma-related injuries are the primary lumbar spine conditions necessitating fusion.
What are the goals of lumbar fusion surgery?
The main objectives are to stabilize the spine, relieve pain, and restore functional capacity.
What materials are typically used in intervertebral fusion devices?
Titanium and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) are commonly used due to their biocompatibility and ability to promote bone growth.
How do fusion devices contribute to spinal stabilization?
They support the vertebral column, promote bony fusion, and ensure effective load distribution to stabilize the spine.
What are the different approaches to lumbar fusion surgery?
The main approaches include Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF), Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF), and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF).