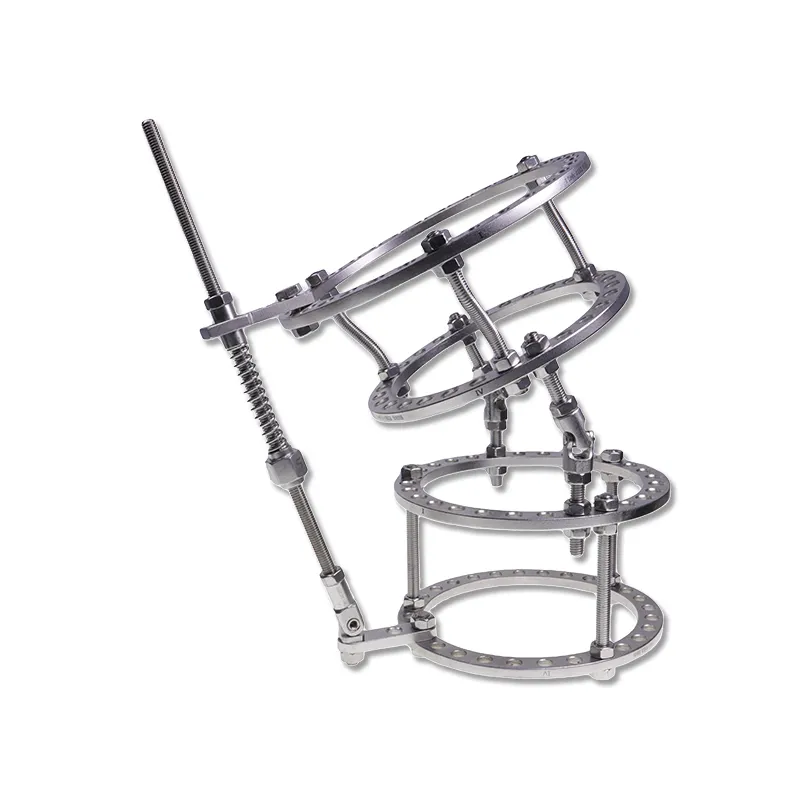
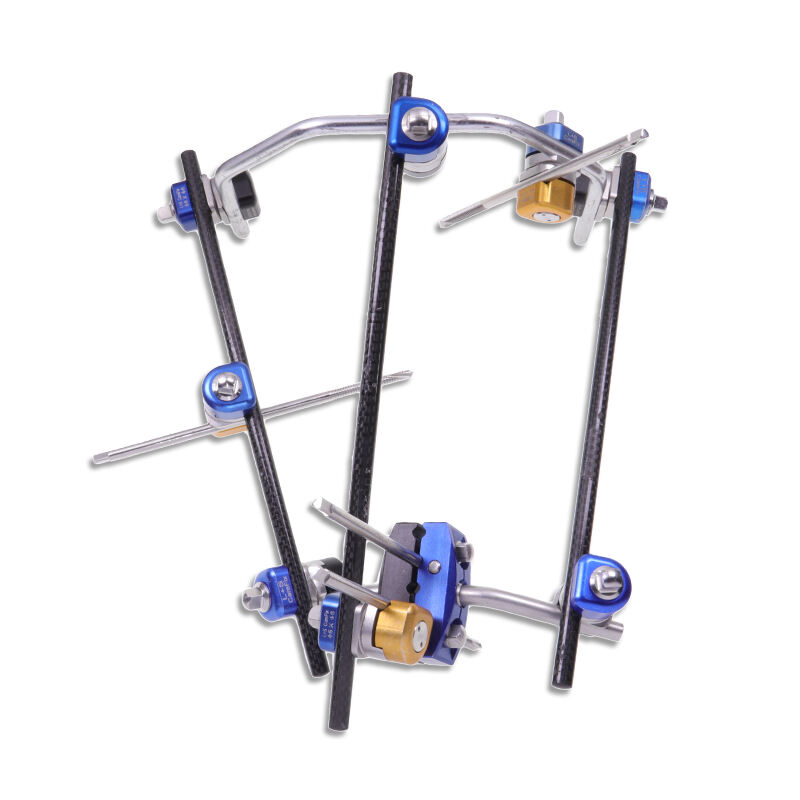
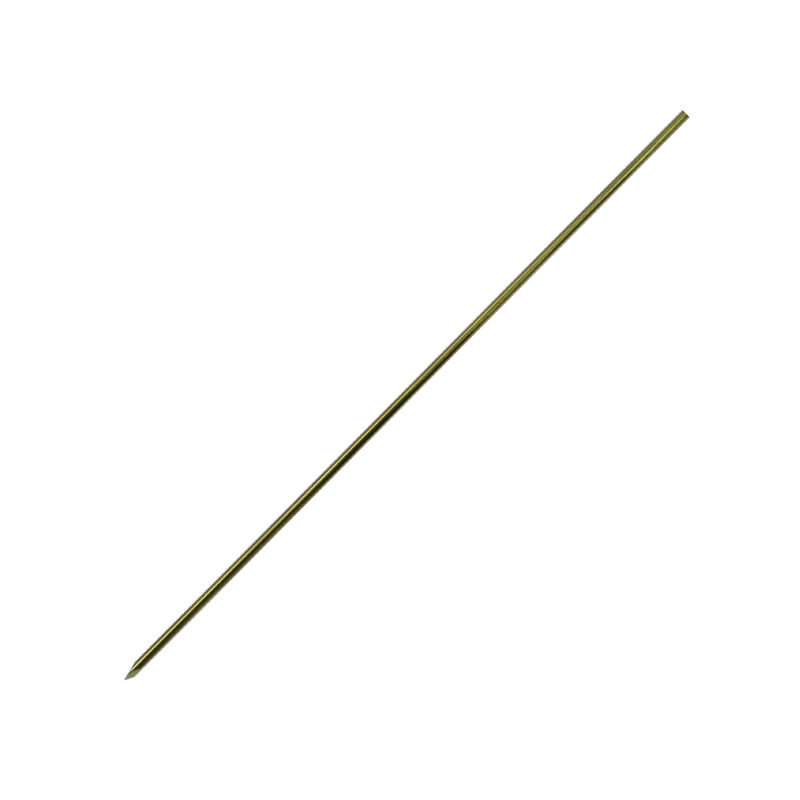
kirschner wire
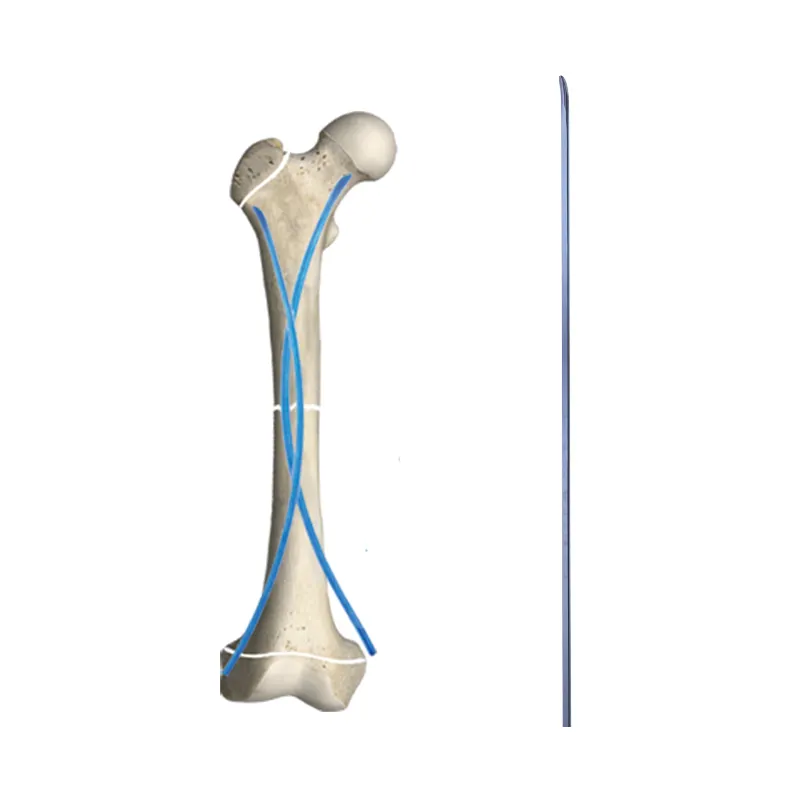
A Kirschner wire, commonly known as a K-wire, is a crucial surgical tool that revolutionized orthopedic procedures since its introduction in the early 20th century. This thin, rigid, metallic pin, typically made from high-grade stainless steel or titanium alloy, serves multiple purposes in modern medical applications. The wire's diameter usually ranges from 0.8mm to 3.0mm, featuring a sharp point at one end for precise penetration through bone tissue. K-wires are fundamental in both temporary and semi-permanent fixation of fractures, particularly in smaller bones of the hands and feet. Their versatility allows surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues while maintaining optimal bone alignment during the healing process. The technology behind K-wires has evolved to include various tip configurations, such as trocar and diamond tips, each designed for specific surgical applications. These wires can be used independently or in conjunction with other fixation devices, making them an indispensable tool in orthopedic surgery. Modern K-wires also feature enhanced surface treatments that improve their biocompatibility and reduce the risk of infection, ensuring better patient outcomes.