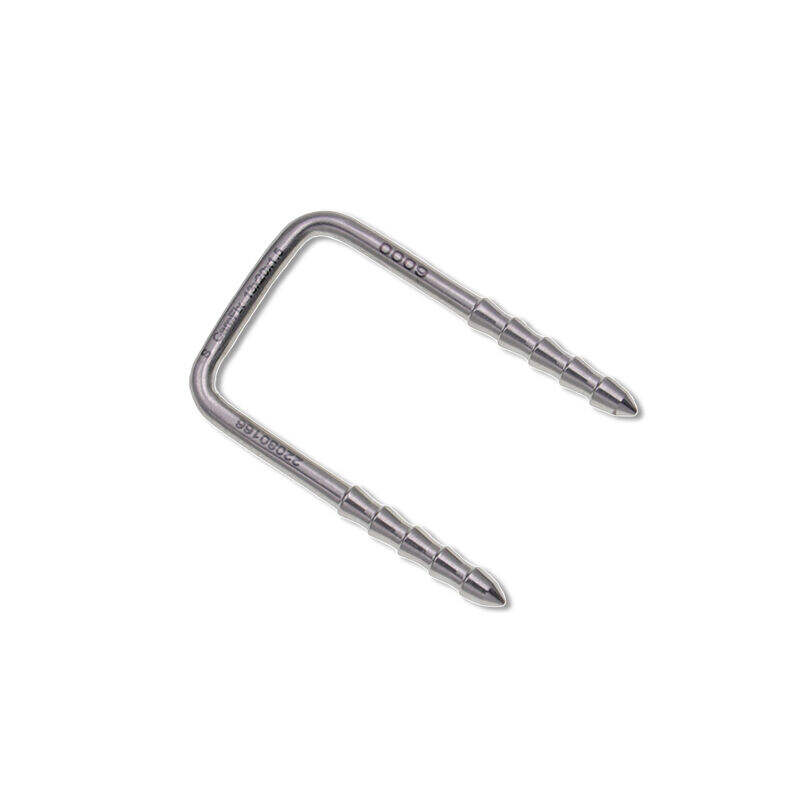
Modern orthopedic surgery has witnessed remarkable advancement in fixation techniques, particularly in the treatment of complex ankle and distal tibial fractures. The distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail represents a significant breakthrough in surgical intervention, offering superior biomechanical stability and enhanced patient outcomes. This innovative fixation system has revolutionized the approach to ankle fusion procedures and complex fracture management, providing surgeons with a reliable tool for achieving optimal bone healing and functional recovery.
Anatomical Design and Biomechanical Excellence
U-Shaped Configuration Benefits
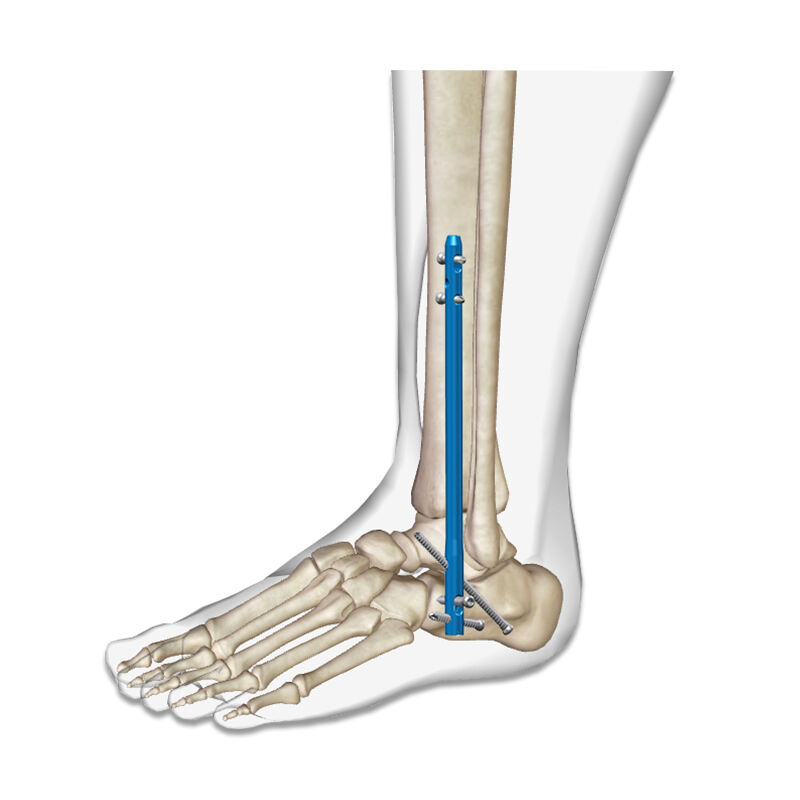
The distinctive U-shaped design of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail provides exceptional biomechanical advantages over traditional fixation methods. This unique curvature follows the natural anatomical contour of the distal tibia, ensuring optimal load distribution throughout the bone structure. The U-shaped profile minimizes stress concentration points that commonly occur with straight nail designs, reducing the risk of implant failure and promoting more uniform healing patterns.
The curved geometry of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail allows for enhanced cortical contact along the medullary canal. This increased surface interaction improves rotational stability and provides superior resistance to bending forces that typically challenge ankle fusion procedures. The design accommodates the natural tibial bow while maintaining proper alignment throughout the healing process.
Material Science and Manufacturing Precision
Contemporary distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail systems utilize advanced titanium alloys that offer optimal biocompatibility and mechanical strength. The manufacturing process employs precision machining techniques to achieve consistent dimensional accuracy and surface finish quality. These materials exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and demonstrate long-term stability within the biological environment.
The surface treatment of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail incorporates specialized coatings that promote osseointegration while reducing inflammatory responses. Advanced manufacturing protocols ensure consistent product quality and dimensional tolerances that meet stringent medical device standards. The material properties provide an ideal balance between strength and flexibility, mimicking natural bone characteristics.
Clinical Applications and Surgical Indications
Ankle Fusion Procedures
The distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail has become the preferred choice for ankle fusion surgeries, particularly in cases involving arthritis, trauma, or congenital deformities. The system provides comprehensive stabilization across the ankle joint while maintaining proper alignment throughout the fusion process. Surgeons report significantly improved fusion rates and reduced complications when utilizing this advanced fixation technique.
Clinical studies demonstrate that the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail achieves superior fusion outcomes compared to traditional plate and screw constructs. The intramedullary positioning provides load-sharing capabilities that reduce stress on the fusion site while promoting natural healing mechanisms. Patient satisfaction rates show marked improvement due to reduced pain and earlier return to functional activities.
Complex Fracture Management
Complex distal tibial fractures present significant challenges in orthopedic surgery, requiring specialized fixation techniques to achieve optimal outcomes. The distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail excels in managing these challenging cases by providing stable fixation while preserving soft tissue integrity. The minimally invasive insertion technique reduces surgical trauma and promotes faster recovery times.
The interlocking mechanism of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail allows for precise control of fracture reduction and maintenance of alignment throughout the healing process. Multiple locking options accommodate various fracture patterns and provide surgeons with flexibility in addressing specific anatomical requirements. The system effectively manages both simple and comminuted fracture patterns with consistent reliability.
Surgical Technique and Implementation
Preoperative Planning Considerations
Successful implementation of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail requires comprehensive preoperative planning and imaging evaluation. Advanced imaging techniques, including computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, provide detailed anatomical information essential for proper nail selection and surgical approach planning. Surgeons must carefully assess bone quality, fracture pattern, and anatomical variations before procedure initiation.
Template matching and sizing protocols ensure optimal fit between the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail and individual patient anatomy. Preoperative planning software allows for virtual implant placement and trajectory optimization, reducing operative time and improving procedural accuracy. Careful consideration of patient factors including bone density, activity level, and healing potential influences implant selection and surgical strategy.
Insertion Technique and Positioning
The insertion technique for the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail follows established protocols that minimize soft tissue disruption while ensuring proper implant positioning. The procedure typically utilizes fluoroscopic guidance to achieve precise nail placement and verify appropriate alignment throughout the insertion process. Specialized instrumentation facilitates accurate drilling and locking screw placement.
Proper positioning of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail requires careful attention to rotational alignment and length measurements. The interlocking mechanism provides multiple fixation points that accommodate various anatomical configurations and fracture patterns. Surgeons must verify secure locking at both proximal and distal ends to ensure optimal stability and prevent implant migration.
Postoperative Management and Recovery
Immediate Postoperative Care
Postoperative management following distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail insertion focuses on pain control, wound care, and early mobilization protocols. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure typically results in reduced postoperative pain and faster recovery compared to traditional open reduction techniques. Patients benefit from shorter hospital stays and earlier return to daily activities.
Immediate postoperative imaging confirms proper positioning of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail and verifies maintenance of alignment. Regular follow-up appointments monitor healing progress and assess for potential complications. Physical therapy protocols are individualized based on patient factors and specific surgical indications.
Long-term Outcomes and Functional Recovery
Long-term outcomes following distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail insertion demonstrate excellent functional recovery and patient satisfaction rates. Clinical studies report high fusion rates and low complication rates across diverse patient populations. The stable fixation provided by the system promotes predictable healing and reduces the need for revision procedures.
Functional assessment tools reveal significant improvements in pain scores, mobility measures, and quality of life indicators following treatment with the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail. Patients typically achieve return to pre-injury activity levels within established timeframes. The durability of the fixation system ensures long-term stability and reduces concerns about implant failure.
Comparative Analysis with Alternative Techniques
Advantages Over Plate Fixation
The distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail offers distinct advantages over traditional plate fixation systems in terms of biomechanical properties and clinical outcomes. The intramedullary position provides superior load-sharing characteristics that reduce stress concentration on fixation hardware. The minimally invasive insertion technique preserves soft tissue integrity and reduces infection risks associated with extensive surgical exposure.
Comparative studies demonstrate lower complication rates and improved healing times when utilizing the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail versus plate and screw constructs. The system eliminates concerns about plate prominence and soft tissue irritation commonly encountered with surface-mounted fixation devices. Patient comfort and functional outcomes show consistent superiority with intramedullary fixation approaches.
Enhanced Stability Compared to External Fixation
External fixation systems, while useful in specific clinical scenarios, present limitations in terms of patient comfort and long-term stability compared to the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail. The internal fixation approach eliminates pin site complications and reduces infection risks associated with transcutaneous hardware. Patients experience improved mobility and quality of life without external hardware restrictions.
The rigid fixation provided by the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail surpasses external fixation in terms of rotational control and axial stability. The internal positioning protects the fixation system from external trauma and environmental factors that may compromise external fixation devices. Long-term outcomes demonstrate superior functional recovery and reduced need for hardware removal procedures.
Innovation and Future Developments
Advanced Imaging Integration
Future developments in distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail technology focus on enhanced imaging integration and computer-assisted surgical techniques. Advanced navigation systems promise improved accuracy in nail placement and reduced radiation exposure during procedures. Three-dimensional planning software continues to evolve, providing surgeons with sophisticated tools for preoperative optimization and intraoperative guidance.
Artificial intelligence applications are being developed to assist in implant selection and surgical planning for distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail procedures. Machine learning algorithms analyze patient-specific factors to recommend optimal implant configurations and predict healing outcomes. These technological advances promise further improvements in surgical precision and patient outcomes.
Biomaterial Enhancements
Research and development efforts continue to advance biomaterial properties for the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail system. Novel surface treatments and coating technologies aim to enhance osseointegration while reducing inflammatory responses. Bioactive materials are being investigated for their potential to promote bone formation and accelerate healing processes.
Smart materials with adaptive properties represent an exciting frontier in distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail design. These materials could potentially adjust their mechanical properties in response to healing progress, providing optimal support throughout the recovery process. Biodegradable components are also under investigation for specific clinical applications where permanent implantation may not be necessary.
FAQ
What makes the U-shaped design of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail superior to straight nails
The U-shaped design follows the natural anatomical curvature of the distal tibia, providing better cortical contact and more uniform load distribution. This configuration reduces stress concentration points and offers superior rotational stability compared to straight nail designs, resulting in improved healing outcomes and reduced risk of implant failure.
How long does recovery typically take after distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail surgery
Recovery times vary based on individual patient factors and specific surgical indications, but most patients begin weight-bearing activities within 6-12 weeks post-surgery. Complete healing and return to full activities typically occurs within 3-6 months, with the minimally invasive nature of the procedure generally resulting in faster recovery compared to traditional fixation methods.
Are there any contraindications for using the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail
Contraindications may include active infection at the surgical site, severe osteoporosis that would compromise fixation, or anatomical abnormalities that prevent proper nail placement. Patients with certain medical conditions affecting bone healing or those unable to comply with postoperative restrictions may not be suitable candidates for this procedure.
What is the long-term durability of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail implant
Clinical studies demonstrate excellent long-term durability with high success rates and low revision rates extending beyond 10 years post-implantation. The titanium alloy construction provides exceptional corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, with most patients experiencing permanent fixation without need for implant removal or revision surgery throughout their lifetime.
Table of Contents
- Anatomical Design and Biomechanical Excellence
- Clinical Applications and Surgical Indications
- Surgical Technique and Implementation
- Postoperative Management and Recovery
- Comparative Analysis with Alternative Techniques
- Innovation and Future Developments
-
FAQ
- What makes the U-shaped design of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail superior to straight nails
- How long does recovery typically take after distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail surgery
- Are there any contraindications for using the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail
- What is the long-term durability of the distal tibial interlocking intramedullary nail implant