Revolutionary Advancements in Pediatric Orthopedic Treatment
Modern pediatric orthopedics has witnessed remarkable progress in surgical techniques and medical devices. Among these innovations, extendable intramedullary needles have emerged as a groundbreaking solution for treating growing children with orthopedic conditions. These sophisticated devices have transformed the approach to managing various pediatric bone disorders, offering unprecedented benefits for both surgeons and young patients.
The implementation of extendable intramedullary needles represents a significant leap forward in addressing the unique challenges of pediatric orthopedic surgery. These specialized devices accommodate bone growth while maintaining structural support, fundamentally changing how we approach long-term orthopedic care in children.
Technical Innovation in Pediatric Orthopedic Devices
Design Features and Functionality
Extendable intramedullary needles incorporate sophisticated engineering principles that allow for controlled lengthening as the child grows. The telescopic design enables smooth extension while maintaining structural integrity throughout the treatment period. The device's innovative mechanism ensures precise adjustment capabilities, allowing orthopedic surgeons to fine-tune the treatment according to each patient's specific growth patterns.
The materials used in manufacturing extendable intramedullary needles meet the highest biocompatibility standards, ensuring long-term safety for pediatric patients. Advanced coating technologies minimize friction and wear, extending the functional lifespan of these devices while reducing the risk of complications.
Surgical Implementation Methods
The surgical technique for implementing extendable intramedullary needles has been refined to minimize invasiveness and optimize outcomes. Surgeons can insert these devices through small incisions, reducing tissue trauma and scarring. The procedure's precision requirements have led to the development of specialized surgical instruments and protocols, enhancing the accuracy of placement and subsequent adjustments.
Modern imaging technologies play a crucial role in the precise positioning of extendable intramedullary needles. Real-time visualization during surgery ensures optimal placement, while post-operative monitoring helps track the device's performance and the bone's response to treatment.
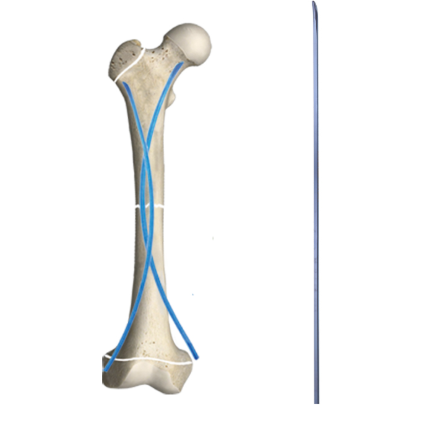
Clinical Benefits and Patient Outcomes
Enhanced Recovery and Rehabilitation
The use of extendable intramedullary needles significantly improves the post-operative recovery experience for pediatric patients. The minimally invasive nature of the procedure results in reduced pain levels and shorter hospital stays compared to traditional surgical approaches. Children typically return to their daily activities more quickly, contributing to better psychological outcomes during the recovery period.
Rehabilitation protocols specifically designed for patients with extendable intramedullary needles focus on maintaining mobility while protecting the treated area. Physical therapy can begin earlier, promoting optimal healing and functional recovery while the device provides necessary structural support.
Long-term Treatment Success
Clinical studies have demonstrated impressive long-term outcomes when using extendable intramedullary needles in pediatric orthopedics. The ability to adjust the device's length in sync with bone growth prevents the need for multiple surgical interventions, reducing the overall physical and emotional impact on young patients. This approach has shown superior results in maintaining limb length equality and proper alignment throughout the growth period.
Follow-up data indicates high patient satisfaction rates and improved quality of life measures among children treated with these devices. The psychological benefits of requiring fewer surgeries and experiencing less disruption to daily activities contribute significantly to these positive outcomes.
Cost-Effectiveness and Healthcare Impact
Economic Considerations
While the initial investment in extendable intramedullary needles may be higher than traditional treatment methods, the long-term cost analysis reveals significant economic benefits. The reduction in multiple surgical procedures, shorter hospital stays, and decreased rehabilitation requirements contribute to overall cost savings for healthcare systems and families.
Insurance providers increasingly recognize the value proposition of these devices, leading to improved coverage policies and accessibility for pediatric patients. The demonstrated reduction in complications and secondary procedures helps justify the initial investment from a healthcare economics perspective.
Healthcare Resource Optimization
The implementation of extendable intramedullary needles helps optimize healthcare resource utilization. Reduced surgical frequency means less operating room time and shorter hospital stays, allowing medical facilities to treat more patients effectively. The streamlined follow-up care requirements also contribute to more efficient use of clinical resources.
Healthcare providers report improved scheduling efficiency and reduced emergency interventions when using these devices, leading to better resource allocation and enhanced patient care delivery.
Future Developments and Research Directions
Technological Advancements
Ongoing research in extendable intramedullary needle technology focuses on incorporating smart materials and sensors for real-time monitoring of bone growth and device performance. These innovations promise to further enhance treatment precision and patient outcomes. Development of bioactive coatings and improved extension mechanisms continues to push the boundaries of what's possible in pediatric orthopedic care.
Integration with digital health platforms and telemedicine applications is enabling better remote monitoring and adjustment capabilities, potentially reducing the frequency of in-person clinical visits while maintaining high standards of care.
Clinical Research Initiatives
Multiple international research collaborations are underway to gather long-term data on the effectiveness of extendable intramedullary needles across different patient populations and conditions. These studies aim to refine treatment protocols and expand the applications of these devices in pediatric orthopedics.
Emerging research also explores the potential use of custom-designed devices based on individual patient characteristics, leveraging advanced manufacturing technologies like 3D printing for optimized outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do extendable intramedullary needles typically last?
Extendable intramedullary needles are designed to function throughout the child's growth period, typically lasting several years. The exact duration depends on the individual patient's growth rate and specific medical condition. Regular monitoring ensures optimal device performance throughout the treatment period.
What age is most suitable for implementing extendable intramedullary needles?
These devices are most commonly used in children between the ages of 5 and 12 years, though the specific timing depends on the individual case, growth potential, and underlying condition. The decision for implementation is made based on careful evaluation of multiple factors by the treating orthopedic team.
Are adjustment procedures painful for the patient?
Most adjustment procedures for extendable intramedullary needles are minimally uncomfortable and can be performed during routine outpatient visits. The process is typically well-tolerated by pediatric patients, and any discomfort can be effectively managed with appropriate pain management strategies.
What types of conditions are most suitable for treatment with these devices?
Extendable intramedullary needles are particularly effective in treating conditions such as limb length discrepancies, bone deformities, and certain types of skeletal dysplasias. They are also valuable in managing complications from trauma or disease affecting bone growth in pediatric patients.