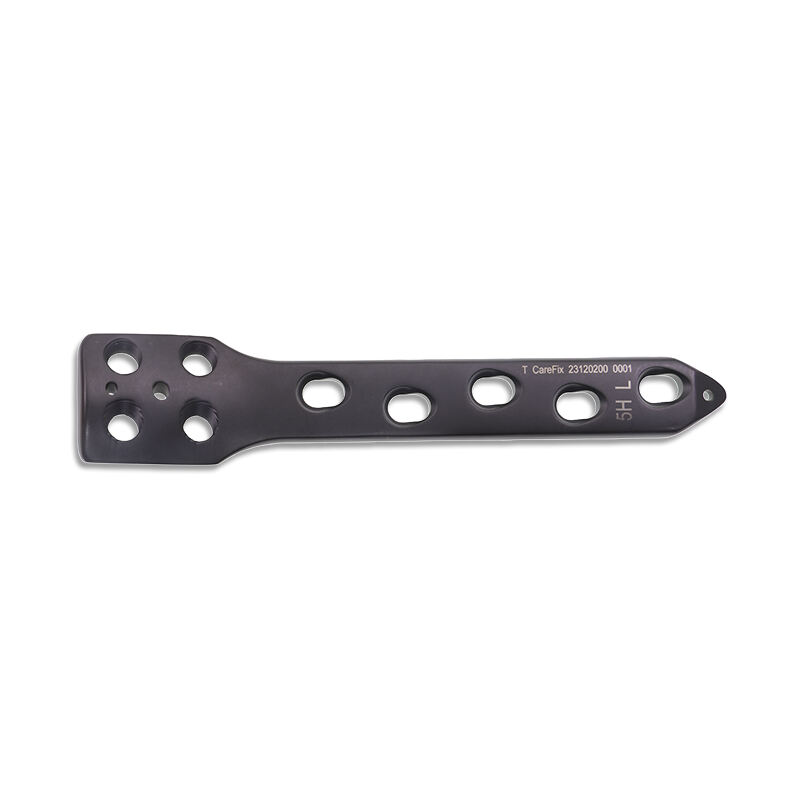
High tibial osteotomy represents one of the most effective surgical interventions for treating knee joint disorders, particularly those involving medial compartment osteoarthritis and varus deformity correction. The success of this procedure largely depends on the quality and precision of the fixation hardware used during surgery. An HTO locking plate provides surgeons with the advanced stability and control necessary for optimal patient outcomes, combining innovative design features with proven biomechanical principles to ensure reliable bone healing and long-term joint function.

Understanding High Tibial Osteotomy Procedures
Surgical Indications and Patient Selection
High tibial osteotomy serves as a joint-preserving procedure designed to redistribute weight-bearing forces across the knee joint by correcting angular deformities. Surgeons typically recommend this intervention for patients under 60 years of age who present with isolated medial compartment osteoarthritis, varus malalignment, and adequate lateral compartment preservation. The procedure involves creating a controlled bone cut in the proximal tibia, followed by precise correction of the mechanical axis to achieve optimal load distribution.
Patient selection criteria include factors such as bone quality, activity level, and the degree of deformity present. Young, active individuals with unicompartmental disease often experience significant pain relief and functional improvement following HTO procedures. The success rate increases substantially when surgeons utilize high-quality fixation systems that provide stable construct stability throughout the healing process.
Biomechanical Principles of Osteotomy Fixation
The biomechanical environment surrounding the proximal tibia presents unique challenges for surgical fixation. Weight-bearing forces during normal gait can exceed three times body weight, creating substantial stress concentrations at the osteotomy site. An HTO locking plate must withstand these cyclic loading conditions while maintaining precise alignment and promoting bone healing through appropriate mechanical stimulation.
Locking plate technology addresses these biomechanical requirements by creating a fixed-angle construct that distributes forces more evenly across the bone-implant interface. This design philosophy reduces the risk of screw loosening, maintains correction angles throughout healing, and provides superior resistance to collapse compared to conventional plating systems. The locked screw-plate interface functions as an internal fixator, offering enhanced stability in challenging bone quality scenarios.
Advanced Design Features of Modern HTO Locking Plates
Material Selection and Manufacturing Excellence
Contemporary HTO locking plate systems utilize medical-grade titanium alloys that offer optimal biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties. Titanium's modulus of elasticity more closely matches that of human bone compared to stainless steel alternatives, reducing stress shielding effects that can compromise long-term bone health. The manufacturing process involves precision machining and surface treatments that enhance osseointegration while maintaining the structural integrity required for demanding orthopedic applications.
Surface modifications such as titanium plasma spray coatings or anodization create microscopic textures that promote cellular attachment and bone ingrowth. These enhanced surfaces contribute to improved implant stability over time, particularly important in HTO procedures where long-term fixation strength directly impacts patient outcomes. Quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process ensure consistent mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy across all plate configurations.
Anatomical Contouring and Screw Trajectory Optimization
Modern HTO locking plate designs incorporate detailed anatomical studies to achieve optimal bone-plate interface contact and minimize soft tissue irritation. Pre-contoured plates reduce surgical time while ensuring predictable fit across diverse patient populations. The plate curvature follows the natural geometry of the proximal tibial metaphysis, providing stable fixation without requiring extensive surgical exposure or soft tissue stripping.
Screw trajectory angles within an HTO locking plate are strategically planned to maximize bone purchase while avoiding critical anatomical structures. Variable angle locking technology allows surgeons to fine-tune screw placement based on individual patient anatomy and bone quality assessment. This flexibility proves particularly valuable in revision scenarios or cases with compromised bone stock where standard trajectories may not provide adequate fixation strength.
Surgical Techniques and Application Methods
Preoperative Planning and Templating
Successful HTO locking plate application begins with comprehensive preoperative planning utilizing advanced imaging and digital templating software. Surgeons analyze weight-bearing radiographs, CT scans, and occasionally MRI studies to determine the precise correction angle required and select appropriate plate size and configuration. Digital templating allows virtual placement of the HTO locking plate to verify screw positioning and predict postoperative alignment before entering the operating room.
Three-dimensional planning software enables surgeons to simulate the osteotomy procedure, calculate opening or closing wedge dimensions, and assess the impact of correction on surrounding joint mechanics. This detailed preparation reduces surgical time, improves accuracy of correction, and minimizes the risk of complications related to improper implant sizing or placement. Patient-specific instrumentation may be fabricated based on preoperative plans to further enhance surgical precision.
Intraoperative Techniques for Optimal Fixation
The surgical approach for HTO locking plate implantation requires careful attention to anatomical landmarks and soft tissue preservation. Surgeons typically utilize a medial approach to the proximal tibia, protecting the common peroneal nerve and maintaining adequate soft tissue coverage over the implant. Precise osteotomy cuts are created using oscillating saws or specialized cutting guides to ensure parallel bone surfaces and optimal contact area for healing.
Plate positioning represents a critical step in the surgical procedure, requiring accurate alignment with the anatomical axis and appropriate distance from joint surfaces. An HTO locking plate must be positioned to allow full range of motion while providing stable fixation across the osteotomy site. Fluoroscopic guidance assists surgeons in confirming proper plate placement and screw trajectory before final tightening of all fixation elements.
Clinical Outcomes and Long-Term Performance
Functional Recovery and Patient Satisfaction
Clinical studies consistently demonstrate favorable outcomes following HTO procedures when performed with high-quality locking plate fixation systems. Patients typically experience significant improvement in pain scores, functional capacity, and quality of life measures within the first year following surgery. The stable fixation provided by an HTO locking plate allows for accelerated rehabilitation protocols and earlier return to activities of daily living compared to less stable fixation methods.
Long-term follow-up studies show maintenance of correction angles and preservation of joint function for periods extending beyond ten years in appropriately selected patients. The durability of modern HTO locking plate systems contributes to these positive outcomes by preventing loss of correction and promoting solid bone union at the osteotomy site. Patient satisfaction rates consistently exceed 85% in most published series, reflecting the effectiveness of this treatment approach for appropriate candidates.
Complication Prevention and Management
The incidence of complications following HTO procedures has decreased significantly with the adoption of locking plate technology and refined surgical techniques. Common complications such as nonunion, loss of correction, and implant failure occur less frequently when surgeons utilize appropriately designed HTO locking plate systems. The enhanced stability provided by locked constructs reduces the risk of mechanical complications while promoting reliable bone healing through optimal biomechanical conditions.
When complications do occur, the modular design of modern HTO locking plate systems facilitates revision procedures if necessary. Additional screws can be added to enhance fixation strength, or alternative plate configurations can be utilized to address specific problem areas. The biocompatible materials used in contemporary implants minimize the risk of adverse tissue reactions while maintaining long-term structural integrity throughout the implant's service life.
Comparative Analysis with Alternative Fixation Methods
Traditional Plating Systems vs. Locking Technology
Conventional compression plates rely on friction between the plate and bone surface to maintain stability, requiring adequate bone quality and precise contouring for optimal performance. In contrast, an HTO locking plate creates a fixed-angle construct that functions independently of bone-plate friction, providing superior stability in osteoporotic bone or challenging anatomical situations. This fundamental difference in fixation philosophy translates to improved clinical outcomes and reduced complication rates in appropriate applications.
The mechanical advantages of locking plate technology become particularly evident in the proximal tibia, where trabecular bone density may be compromised and cyclic loading conditions are severe. Traditional plates may experience screw loosening or loss of reduction over time, while locking systems maintain their initial stability throughout the healing process. The enhanced resistance to toggle and micromotion provided by locked constructs promotes more predictable bone healing and better long-term outcomes.
External Fixation Alternatives
External fixation systems offer certain advantages for HTO procedures, including the ability to make gradual corrections and avoid permanent implant placement. However, these systems also present challenges related to pin site infections, patient comfort, and prolonged treatment duration. An HTO locking plate provides immediate stable fixation that allows for faster rehabilitation and eliminates the complications associated with transcutaneous pin placement.
The decision between internal and external fixation often depends on patient factors such as bone quality, compliance with postoperative restrictions, and the complexity of the deformity being corrected. Internal fixation with HTO locking plate systems generally offers superior patient acceptance and functional outcomes, while external fixation may be preferred in complex deformity cases requiring gradual correction or in patients with compromised soft tissue conditions.
Future Developments and Innovations
Smart Implant Technology Integration
The future of HTO locking plate design includes integration of smart technologies that can monitor healing progress and provide real-time feedback to surgeons and patients. Sensor-equipped implants capable of measuring load distribution, bone healing status, and range of motion parameters represent the next evolution in orthopedic hardware. These advanced systems will enable personalized rehabilitation protocols and early detection of potential complications before they become clinically apparent.
Bioactive coatings and drug-eluting surfaces represent another frontier in HTO locking plate development. These technologies could enhance bone healing rates, reduce infection risk, and improve long-term implant integration through controlled release of growth factors or antimicrobial agents. The combination of mechanical excellence with biological enhancement promises to further improve outcomes for patients undergoing HTO procedures.
Personalized Medicine and Custom Implants
Advances in medical imaging and additive manufacturing technologies are enabling the development of patient-specific HTO locking plate designs tailored to individual anatomical variations. Custom implants can optimize bone-plate interface contact, minimize soft tissue irritation, and provide ideal screw trajectories based on preoperative planning studies. This personalized approach may further improve outcomes while reducing surgical complexity and operative time requirements.
Three-dimensional printing capabilities allow for cost-effective production of patient-specific instrumentation and implants, making personalized orthopedic care more accessible to broader patient populations. As these technologies mature and become more widely available, the standard of care for HTO procedures will continue to evolve toward increasingly precise and individualized treatment approaches.
FAQ
How long does an HTO locking plate remain in the body after surgery
An HTO locking plate is typically designed to remain permanently in the body unless complications arise that require removal. Most patients do not experience any issues with the implant long-term, and removal is generally only considered if the plate causes persistent pain, interferes with daily activities, or develops mechanical problems. The biocompatible materials used in modern plates are well-tolerated by the human body for decades.
What factors determine the success rate of HTO procedures using locking plates
Success rates for HTO procedures depend on several factors including patient age, bone quality, degree of deformity correction required, and adherence to postoperative rehabilitation protocols. Patients under 60 years of age with isolated medial compartment arthritis typically achieve the best outcomes. The quality of the HTO locking plate and surgical technique also significantly influence long-term success rates, which generally exceed 85% in appropriately selected candidates.
Can patients return to high-impact sports after HTO surgery with locking plate fixation
Return to high-impact activities following HTO surgery varies depending on individual healing progress, bone quality, and the specific demands of the sport. Most patients can resume low-impact activities within 3-6 months, while return to high-impact sports may require 6-12 months of recovery. The stable fixation provided by an HTO locking plate allows for more aggressive rehabilitation protocols compared to other fixation methods, potentially enabling faster return to desired activity levels.
What are the signs of potential complications with HTO locking plate implants
Patients should monitor for signs such as persistent or increasing pain, swelling, redness, or drainage around the surgical site, which may indicate infection or implant-related problems. Loss of correction angle, decreased range of motion, or mechanical symptoms such as clicking or grinding may suggest issues with the HTO locking plate or bone healing. Any concerning symptoms should be promptly evaluated by the treating surgeon to ensure optimal outcomes and address potential complications early.
Table of Contents
- Understanding High Tibial Osteotomy Procedures
- Advanced Design Features of Modern HTO Locking Plates
- Surgical Techniques and Application Methods
- Clinical Outcomes and Long-Term Performance
- Comparative Analysis with Alternative Fixation Methods
- Future Developments and Innovations
-
FAQ
- How long does an HTO locking plate remain in the body after surgery
- What factors determine the success rate of HTO procedures using locking plates
- Can patients return to high-impact sports after HTO surgery with locking plate fixation
- What are the signs of potential complications with HTO locking plate implants