Modern Advancements in Surgical Orthopedic Equipment
The landscape of orthopedic surgery continues to evolve rapidly, with technological innovations constantly reshaping the way procedures are performed. Orthopedic instruments have become increasingly sophisticated, combining precision engineering with ergonomic design to enhance surgical outcomes. As we approach 2025, understanding the essential tools and equipment that define modern orthopedic surgery becomes crucial for healthcare professionals and medical facilities.
The foundation of successful orthopedic procedures lies in having access to the right orthopedic instruments. From basic hand tools to complex powered equipment, each instrument serves a specific purpose in the intricate world of bone and joint surgery. This comprehensive guide explores the must-have tools, emerging technologies, and best practices for maintaining a state-of-the-art orthopedic surgical setup.
Core Categories of Orthopedic Surgical Equipment
Manual Cutting and Dissection Tools
At the heart of every orthopedic procedure are the fundamental cutting and dissection instruments. Surgical scissors, osteotomes, and bone-cutting forceps form the backbone of any orthopedic toolkit. These manual instruments require exceptional craftsmanship and regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance during critical procedures.
Modern orthopedic instruments in this category often feature ergonomic handles, titanium-coated blades, and precise calibration markings. The evolution of materials science has led to the development of lightweight yet durable tools that reduce surgeon fatigue during lengthy procedures while maintaining exceptional cutting precision.
Powered Surgical Systems
Power tools represent a significant advancement in orthopedic surgery. High-speed drills, saws, and reaming systems have revolutionized the way surgeons approach bone preparation and modification. These powered orthopedic instruments typically feature modular designs with interchangeable attachments, offering versatility across different surgical scenarios.
The latest generation of powered systems incorporates sophisticated control mechanisms, allowing for precise speed and torque adjustment. Many now include safety features such as automatic shutoff systems and improved cooling mechanisms to prevent tissue damage during prolonged use.
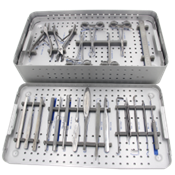
Specialized Instrumentation for Joint Replacement
Hip Replacement Equipment
Hip arthroplasty requires a specific set of orthopedic instruments designed for precise implant positioning and bone preparation. Custom reamers, broaches, and alignment guides ensure accurate component placement. Modern hip replacement tools often incorporate computer-assisted navigation capabilities, improving surgical accuracy and patient outcomes.
Advanced measurement tools and digital templating systems have become essential companions to traditional instruments, allowing surgeons to plan and execute procedures with unprecedented precision. These technologies help optimize implant sizing and positioning while minimizing the risk of complications.
Knee Surgery Instrumentation
The complexity of knee replacement surgery demands specialized orthopedic instruments that facilitate precise bone cuts and accurate ligament balancing. Contemporary knee systems include adjustable cutting blocks, tension meters, and trial components that help surgeons achieve optimal mechanical alignment.
Digital assistance tools have become increasingly integrated with traditional knee surgery instruments, offering real-time feedback on alignment and balance. This combination of classic and modern technology helps ensure consistent surgical outcomes across different patient anatomies.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Tools
Arthroscopic Equipment
Arthroscopic orthopedic instruments have transformed the approach to joint surgery, enabling less invasive procedures with faster recovery times. High-definition cameras, specialized probes, and miniaturized cutting tools allow surgeons to perform complex procedures through small incisions.
The evolution of arthroscopic technology continues to produce more refined instruments, including enhanced visualization systems and specialized tools for tissue manipulation. These advancements have expanded the range of procedures that can be performed arthroscopically.
Navigation and Imaging Systems
Modern orthopedic surgery increasingly relies on advanced navigation and imaging tools. These systems work in conjunction with traditional orthopedic instruments to provide real-time guidance and feedback during procedures. 3D imaging capabilities and augmented reality overlays help surgeons maintain precise control throughout complex operations.
Integration of artificial intelligence with surgical navigation systems represents the cutting edge of orthopedic technology, offering predictive assistance and automated measurements that enhance surgical accuracy.
Instrument Care and Maintenance
Sterilization Protocols
Proper sterilization of orthopedic instruments is crucial for patient safety and instrument longevity. Modern sterilization systems must accommodate both traditional steel instruments and sophisticated electronic components. Healthcare facilities must maintain strict protocols for cleaning, sterilizing, and tracking surgical equipment.
Advanced tracking systems using RFID technology help maintain accurate records of instrument usage and sterilization cycles, ensuring compliance with safety standards and extending the service life of valuable surgical tools.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Regular maintenance of orthopedic instruments is essential for maintaining their precision and reliability. This includes routine inspection, sharpening of cutting tools, and calibration of powered equipment. Healthcare facilities must establish comprehensive maintenance schedules and documentation systems.
Implementing predictive maintenance programs using digital monitoring systems helps prevent unexpected instrument failures and ensures optimal performance during critical procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most essential orthopedic instruments for a new surgical facility?
A new surgical facility should prioritize acquiring a comprehensive set of basic hand instruments, power tools, and specialized equipment for common procedures. This typically includes basic cutting and holding instruments, power drills and saws, arthroscopic equipment, and essential measurement tools. The specific selection should be based on the types of procedures the facility plans to perform.
How often should orthopedic instruments be replaced?
The replacement frequency depends on usage patterns, maintenance quality, and manufacturer recommendations. Generally, manual instruments should be inspected after each use and replaced when signs of wear become apparent. Powered equipment typically requires replacement or major servicing every 3-5 years, depending on usage intensity and maintenance history.
What innovations in orthopedic instruments are expected by 2025?
The field of orthopedic instrumentation is rapidly evolving, with expected innovations including more sophisticated robotic assistance systems, enhanced 3D printing applications for custom instruments, improved navigation technologies, and smarter powered tools with integrated feedback systems. These developments will likely focus on improving precision, reducing invasiveness, and enhancing surgical outcomes.