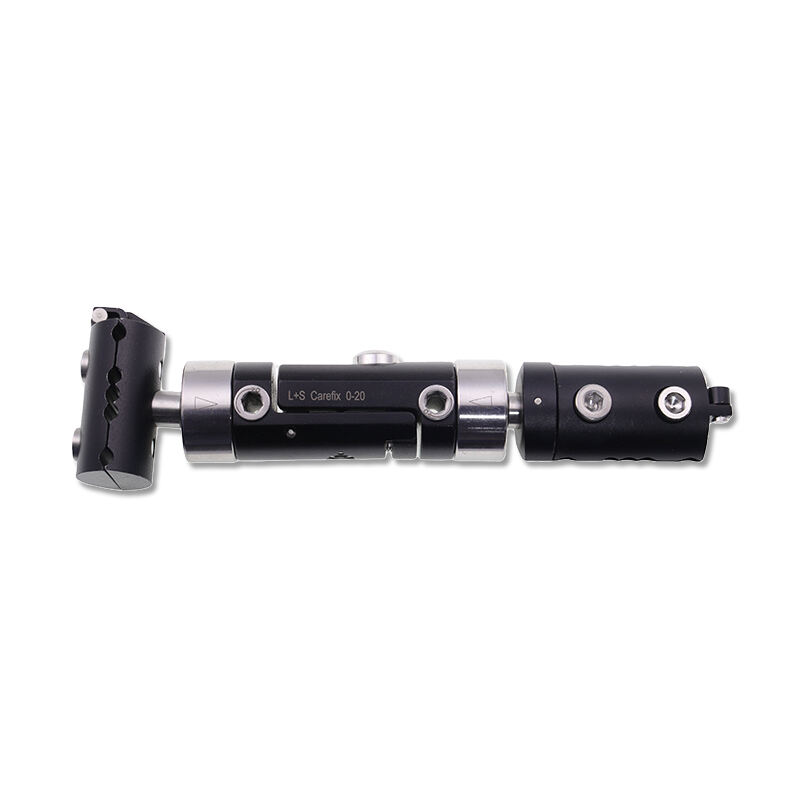
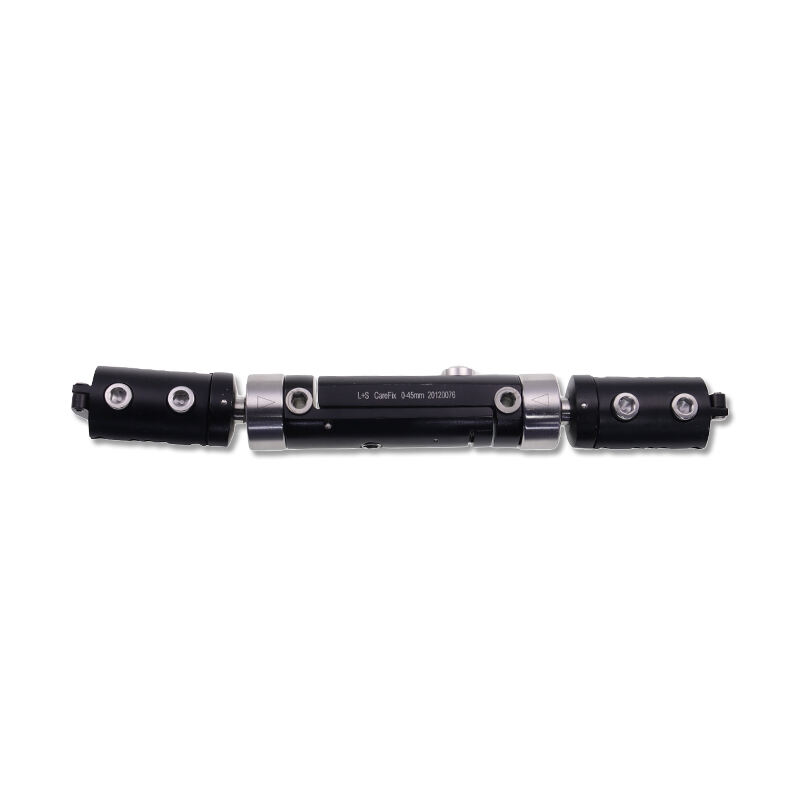
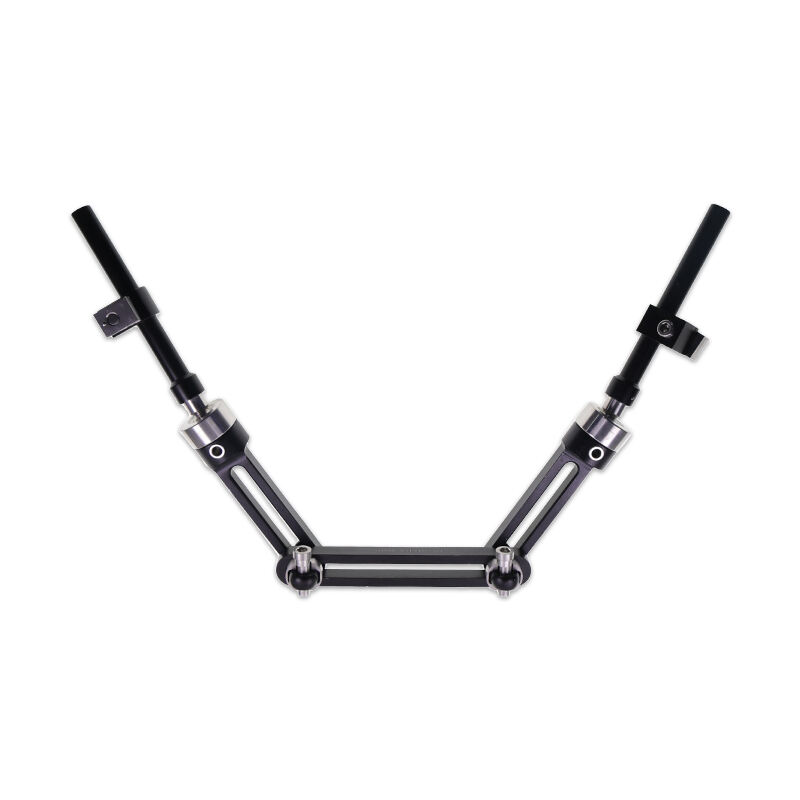
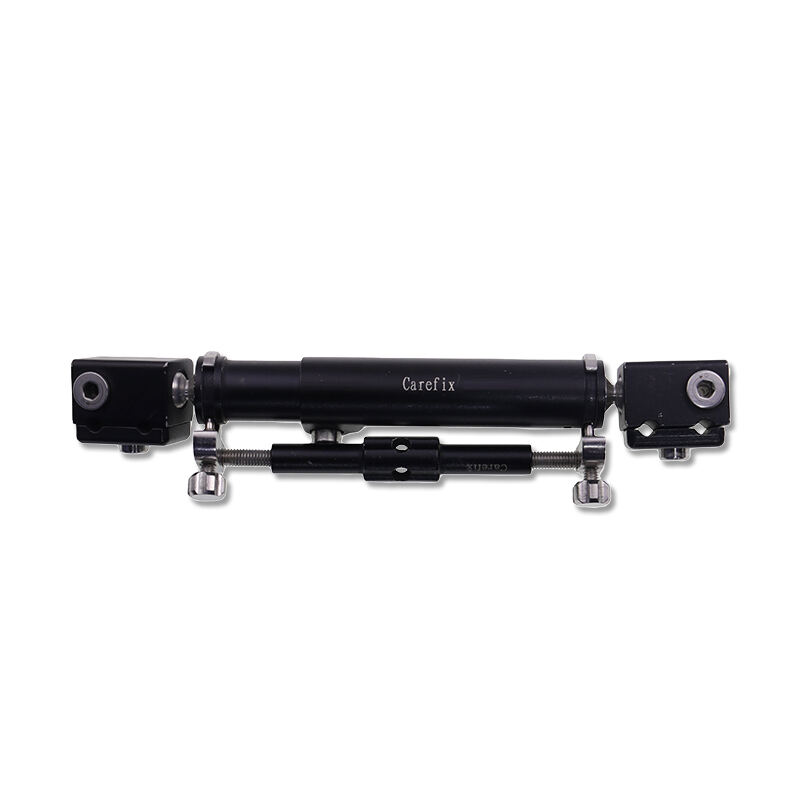
instruments used in orthopedics
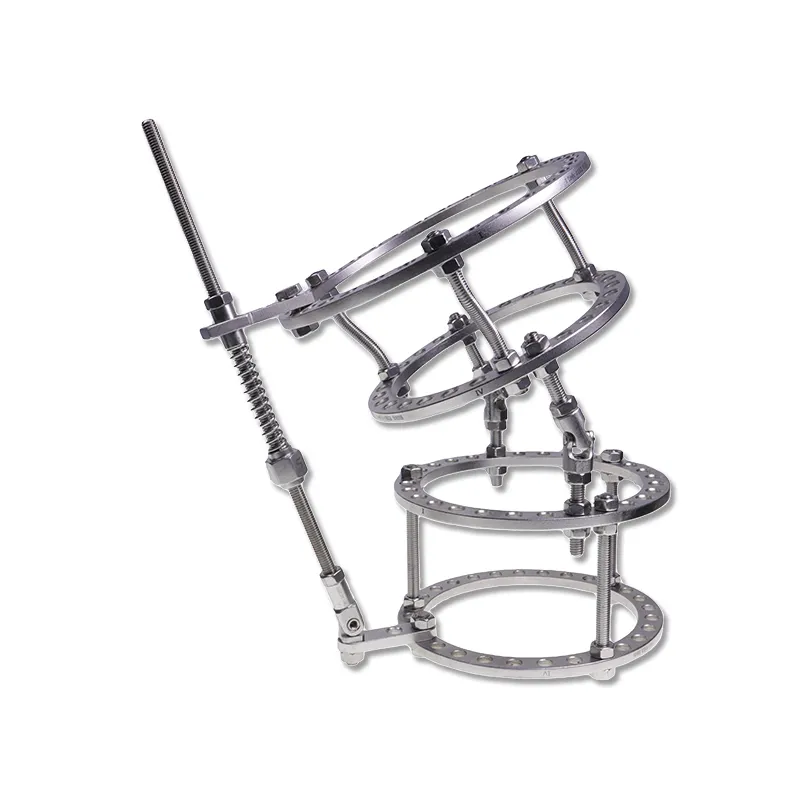
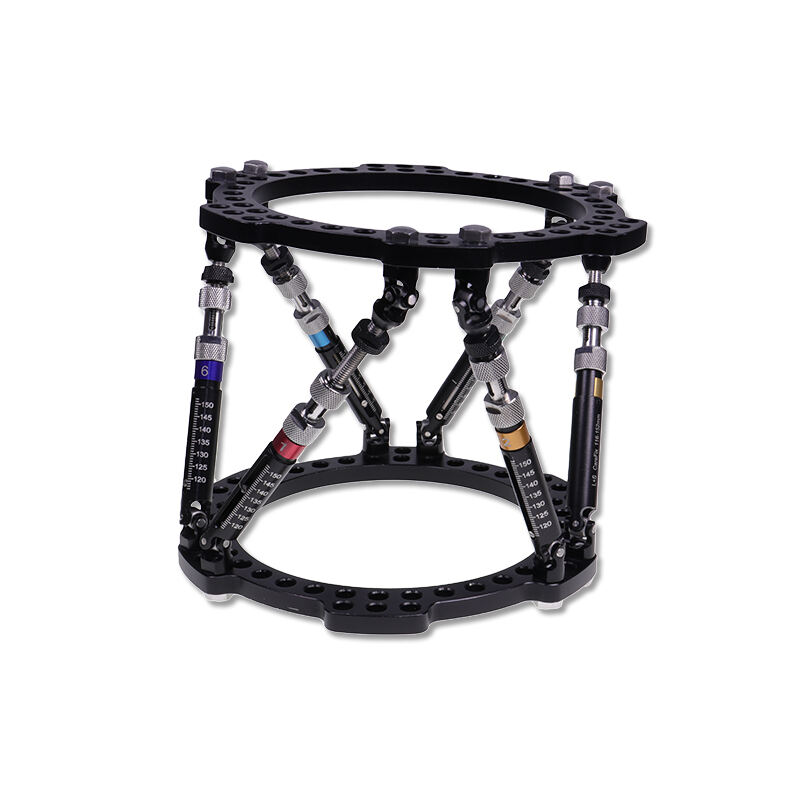
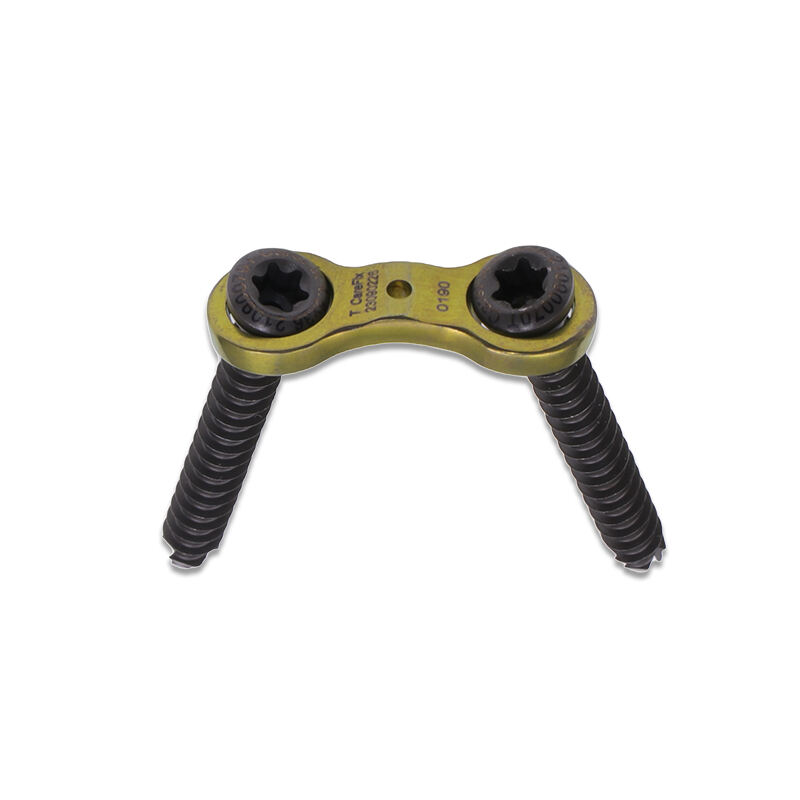
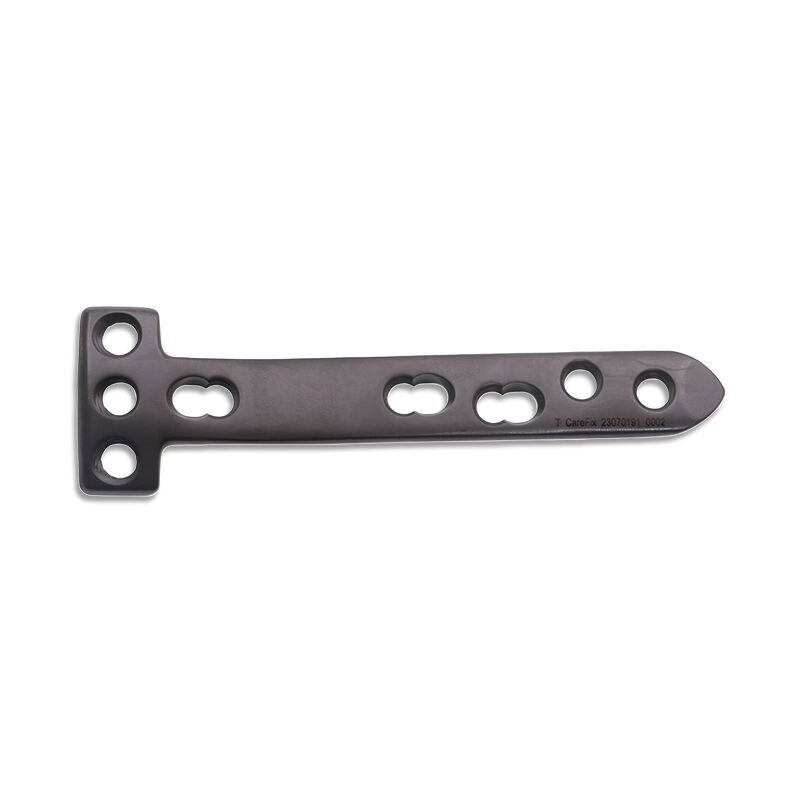
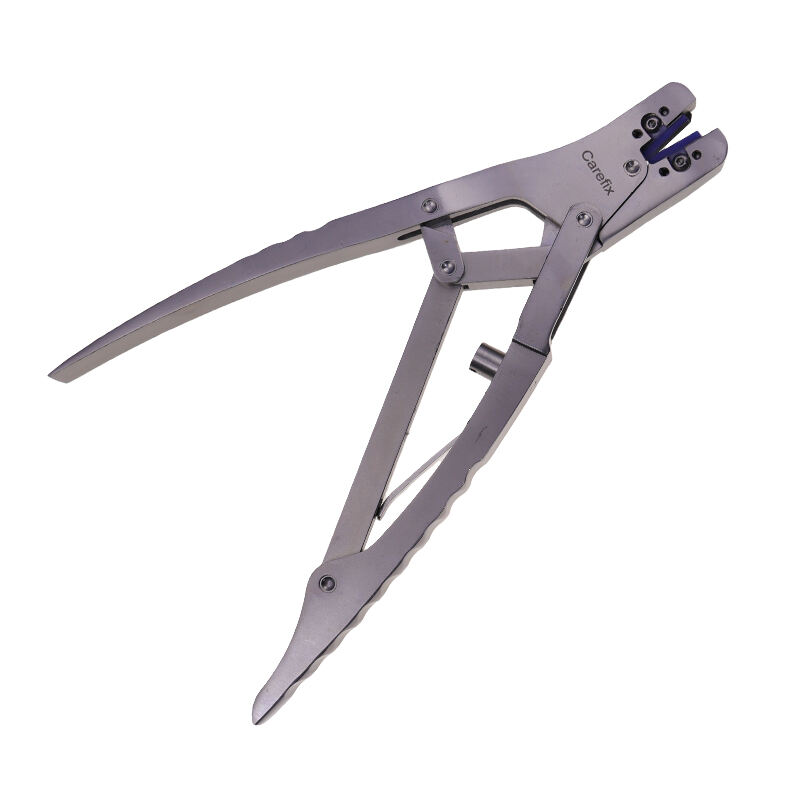
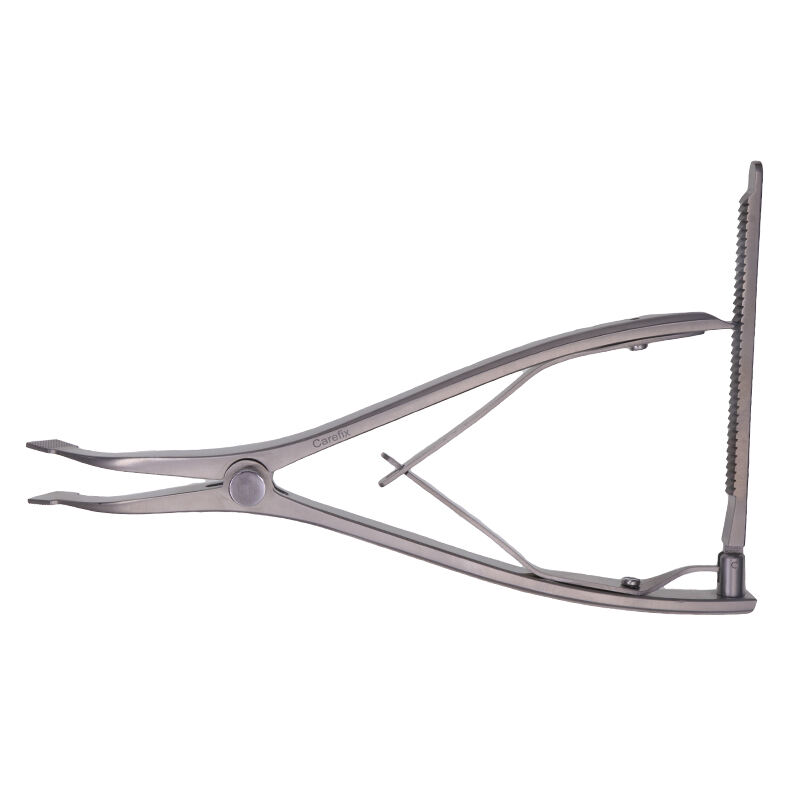
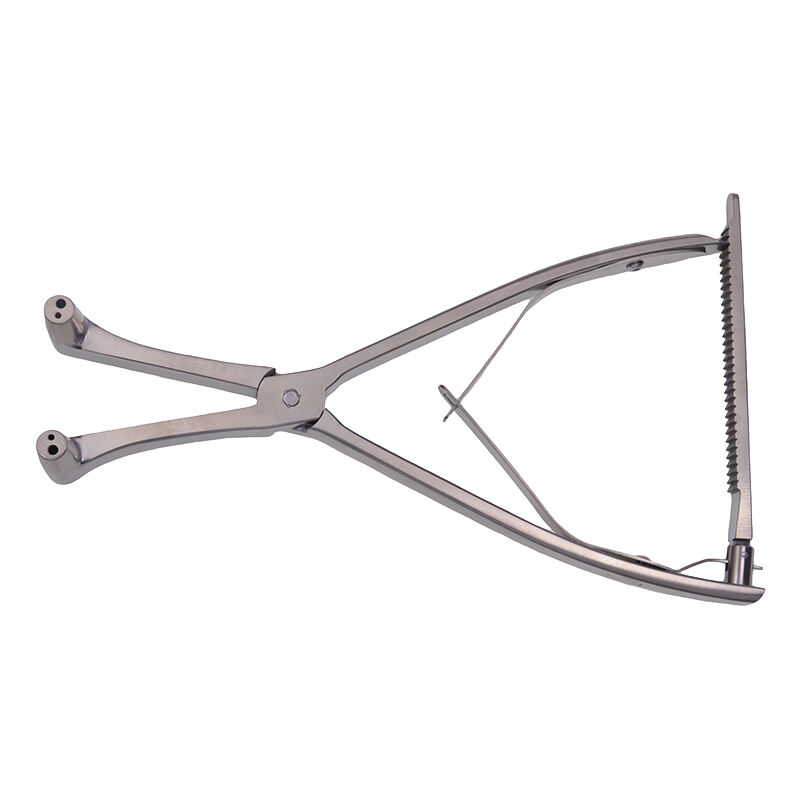
Orthopedic instruments represent a sophisticated array of specialized tools designed for musculoskeletal procedures and treatments. These instruments include precision devices such as bone cutting tools, drills, saws, and specialized implant placement instruments. Modern orthopedic instruments incorporate advanced materials like surgical-grade stainless steel and titanium, ensuring durability and reliability in critical procedures. Digital navigation systems and computer-assisted surgical instruments have revolutionized orthopedic procedures, offering enhanced precision and improved patient outcomes. Power tools in orthopedic surgery, including oscillating saws and high-speed drills, feature ergonomic designs and safety mechanisms to prevent tissue damage. Arthroscopic instruments, equipped with high-definition cameras and specialized cutting tools, enable minimally invasive procedures. These instruments are designed with strict adherence to sterilization standards, featuring materials and construction methods that withstand repeated autoclaving. Measurement instruments, such as depth gauges and sizing guides, ensure accurate implant selection and placement. The evolution of orthopedic instruments continues to advance with the integration of smart technologies, providing real-time feedback and improved surgical accuracy.